GCSE Wind and Solar
Wind
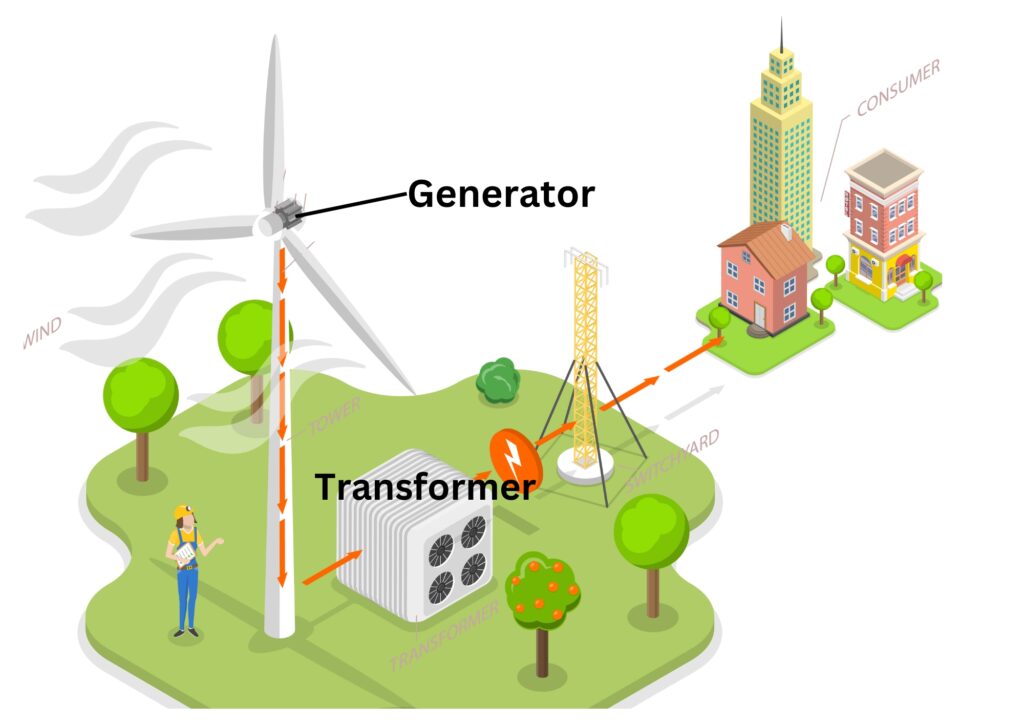
The wind will make the turbine blades move in a circular pattern, which turns a generator to produce electricity.
Kinetic energy store of the wind is mechanically converted to kinetic energy store of the generator. The kinetic energy store of the generator causes electricity to be produced, which is transferred electrically.
The electricity produced can be used for:
Heating of homes with electric heaters
Transportation (electric vehicles)
Electrical appliances
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| No carbon dioxide produced | Can be noisy |
| Once set up, low cost | Unreliable due to variable wind speed |
| Low maintenance | Only suitable in certain locations |
| Birds cannot see blades spinning | |
| Need a lot of wind turbines to generate electricity, low energy density. |
Solar cells

Solar cells use sunlight and convert it into electricity.
The nuclear energy store in the Sun is transferred by radiation to the Solar cells, when then produce electricity.
The electricity can be used for:
Heating of homes with electric heaters
Transportation (electric vehicles)
Electrical appliances
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| No carbon dioxide produced | Initial high cost |
| Low maintenance once installed | Low energy density |
| unreliable |
Solar heating panels, or Solar panels
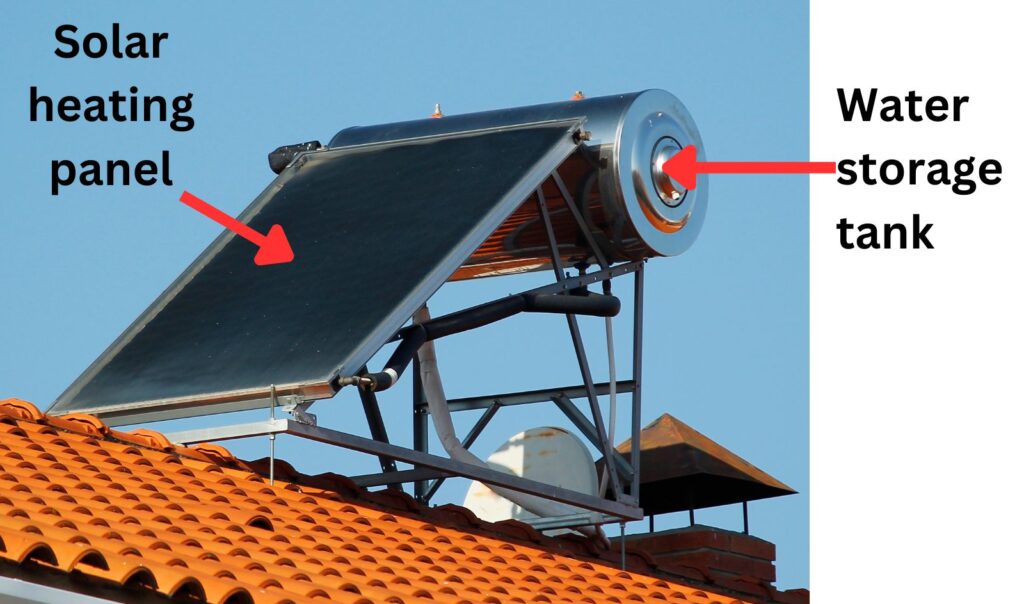

The solar heating panel contains water in pipes, which absorb thermal energy from the Sun’s radiation. This hot water is then supplied to the house.
NOTE the difference between solar panels and solar cells.
Thermal energy store of the Sun is transferred by radiation to the thermal energy store of the water in the pipes.
The energy is used to provide heating in homes and to provide hot water for washing and cleaning.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| No carbon dioxide produced | Initial cost is high |
| Low maintenance once installed | Low energy density |
| Unreliable, they can only supply about 60% of the hot water needed for a house |
Practice Questions
1. Describe the difference between solar cells and solar heating panels
2. Why would solar be considered to be an unreliable energy resource
3. What can the electricity be used for that is generated?
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations