GCSE Thermistors and Light Dependent Resistors
Thermistors
A thermistor is a temperature dependent resistor. As temperature increases, resistance decreases, so there is an inversely proportional relationship.
Note that this is different to a standard wire, where if temperature increases, resistance increases.
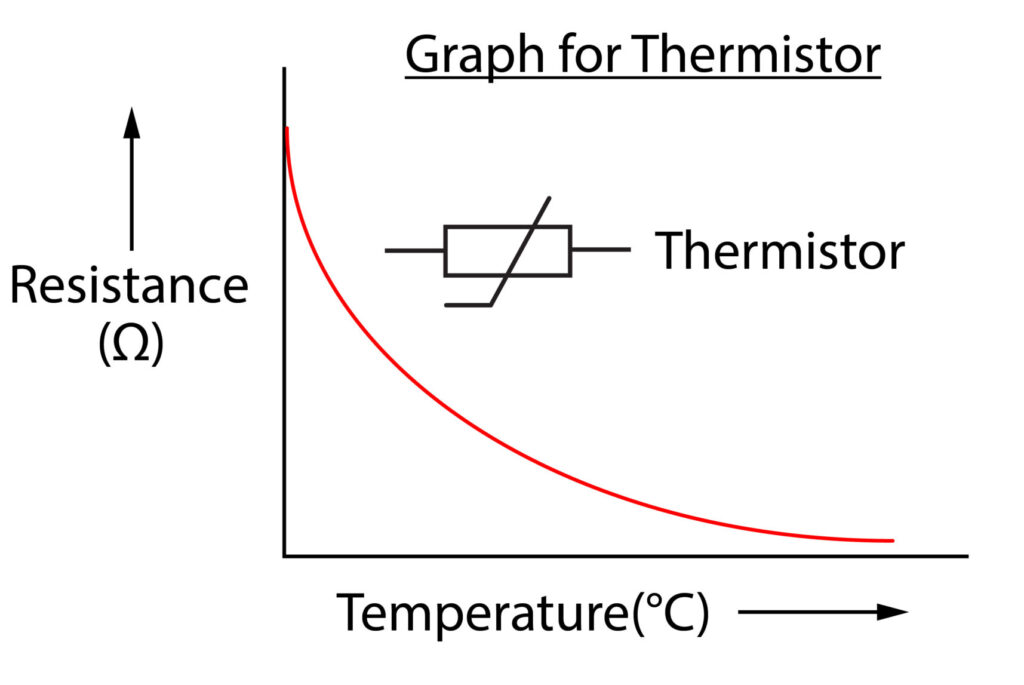
Thermistors are used as thermostats in devices to help to monitor and regulate temperature. When the temperature reaches a certain value the thermistor can change its resistance to switch on or switch off the device.
Devices that contain thermistors include:
1. Temperature regulated incubators
2. Thermostat in ovens
3. Room thermostat for heating systems
4. Engine cooling systems for cars
5. Digital thermometers
Light Dependent Resistor
As light intensity increases, resistance decreases. This is an inversely proportional relationship.
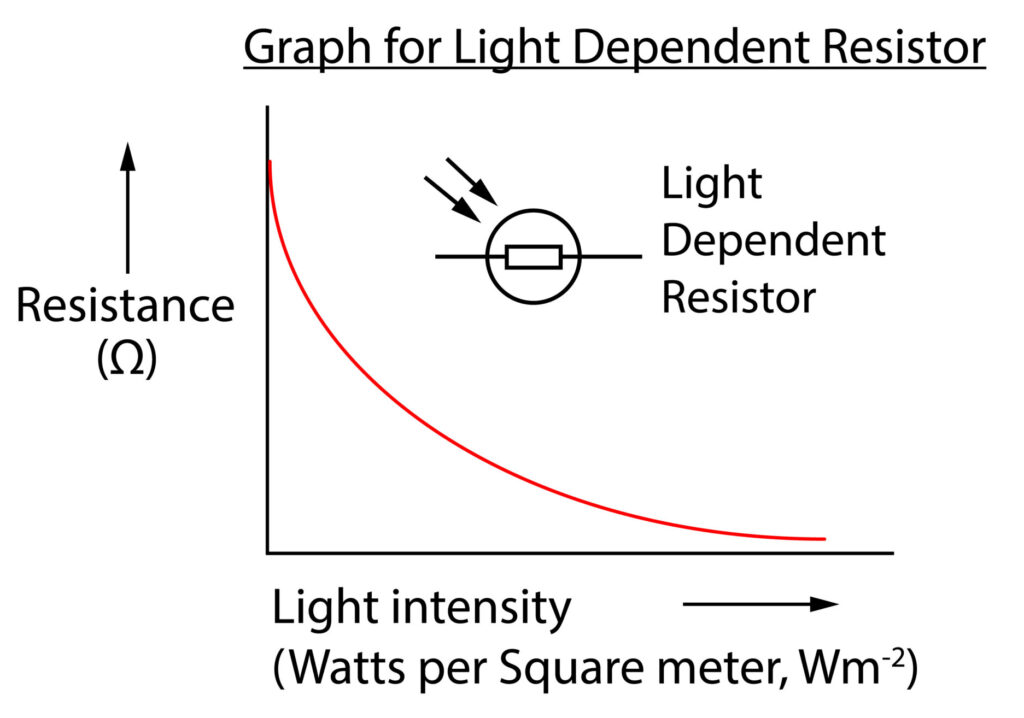
Light dependent resistors can be used to monitor light levels and then switch a circuit on or off.
Light dependent resistors are used in:
1.Automatic night lights, which switch on at night and switch off at dawn.
2. Smoke detectors which detect changes in light intensity
3. Cameras contain light dependent resistors to indicate the amount of light present.
Practice Question
1.Describe how the graph for the thermistor and light dependent resistor are similar
2. Draw a graph of resistance vs 1/temperature for a thermistor
3. Draw a circuit to show how a thermistor can be used to switch on an air conditioning unit when the room temperature becomes too high.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations