GCSE Series Circuit
Series Circuit
A series circuit is a single loop circuit, and the components are connected along a single path, end to end.
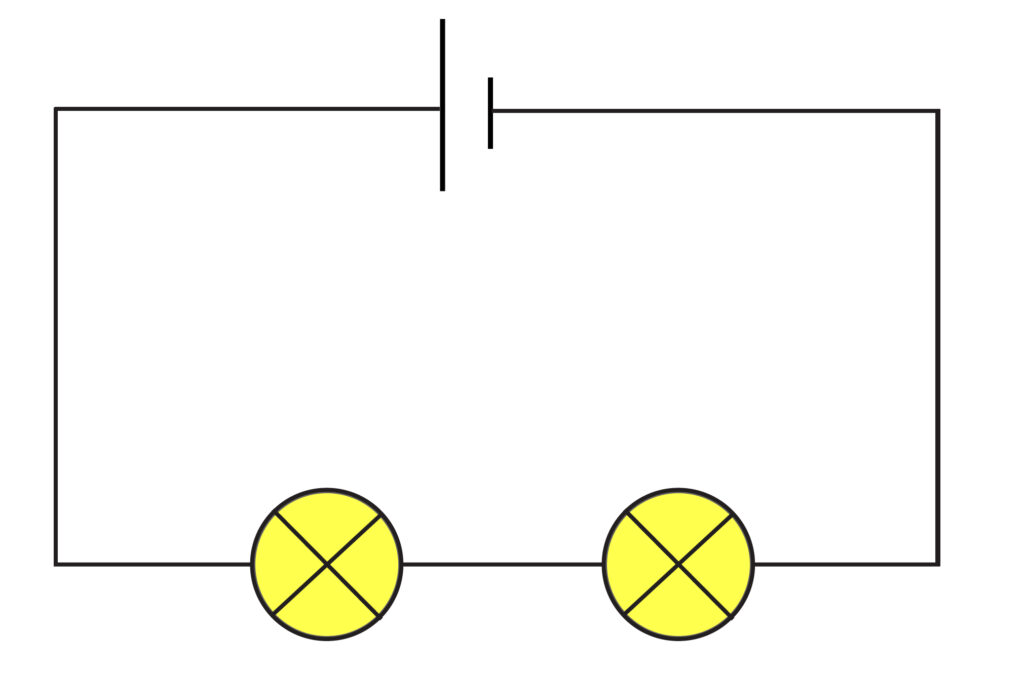
Above is an example of a series circuit with two bulbs.
Series Circuit Rules
Rule 1: In a series circuit, the current is the same at all points.
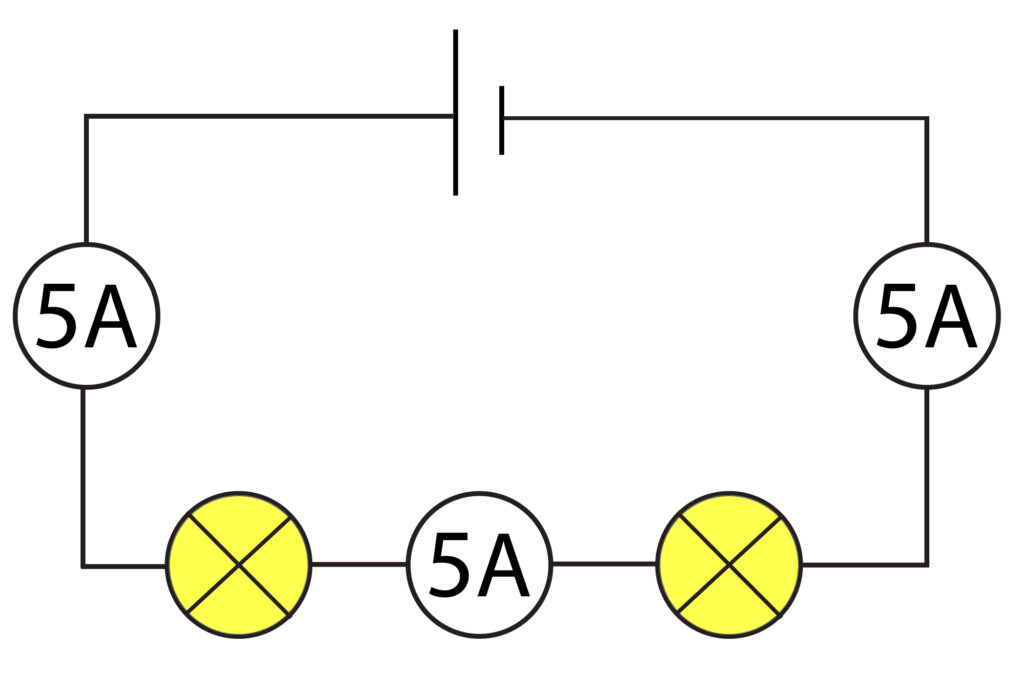
In the above circuit the current is at 5 Amps at all 3 ammeters.
Rule 2: In a series circuit the potential difference is shared between the components.
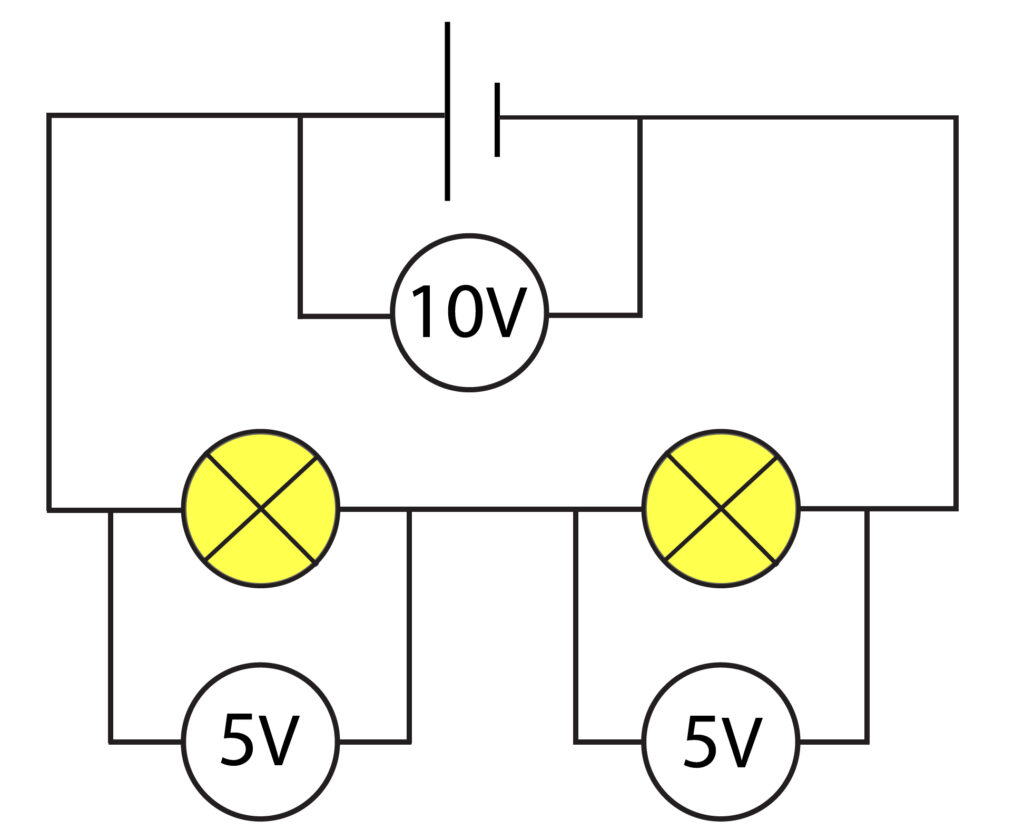
In the above circuit, the 10V potential difference across the cell is shared between the two bulbs equally. So the potential difference across each bulb is 5V.
Rule 3: The total resistance in a series circuit is the sum of the individual resistors.
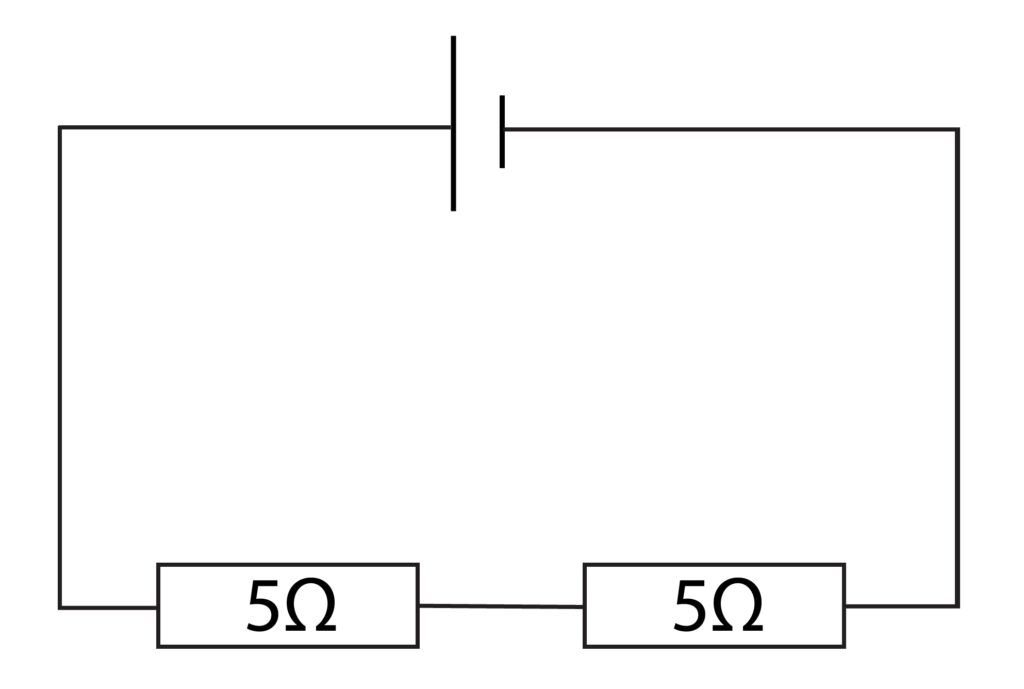
In the above circuit, there are two 5 ohm resistors. So, the total resistance is 10 ohms.
Practice Questions
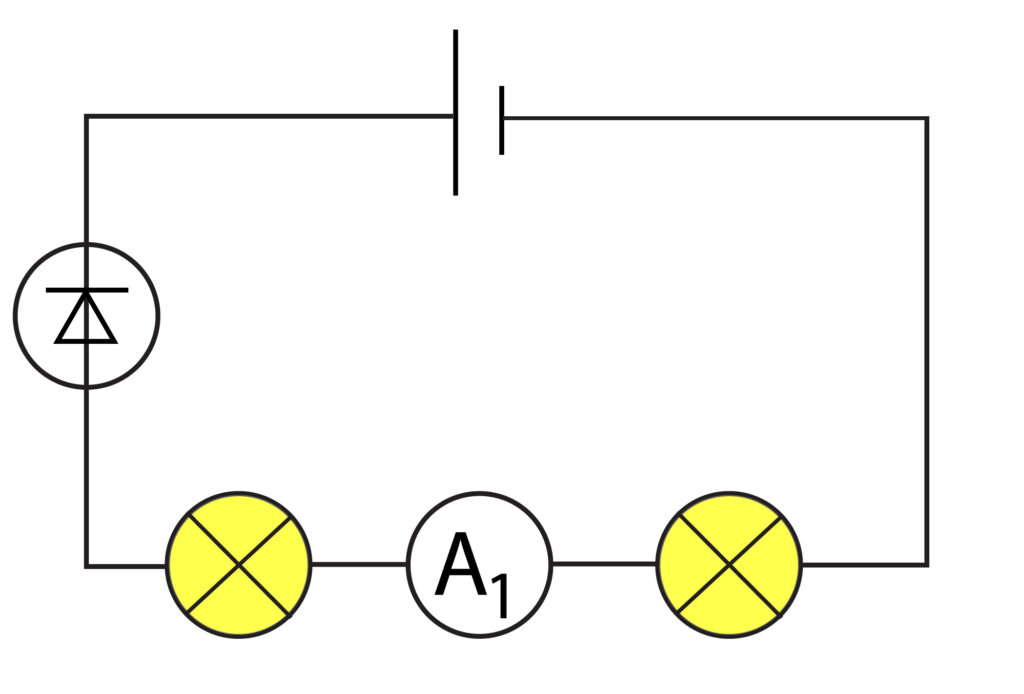
1.State the value for the current for ammeter A1 in the circuit below:
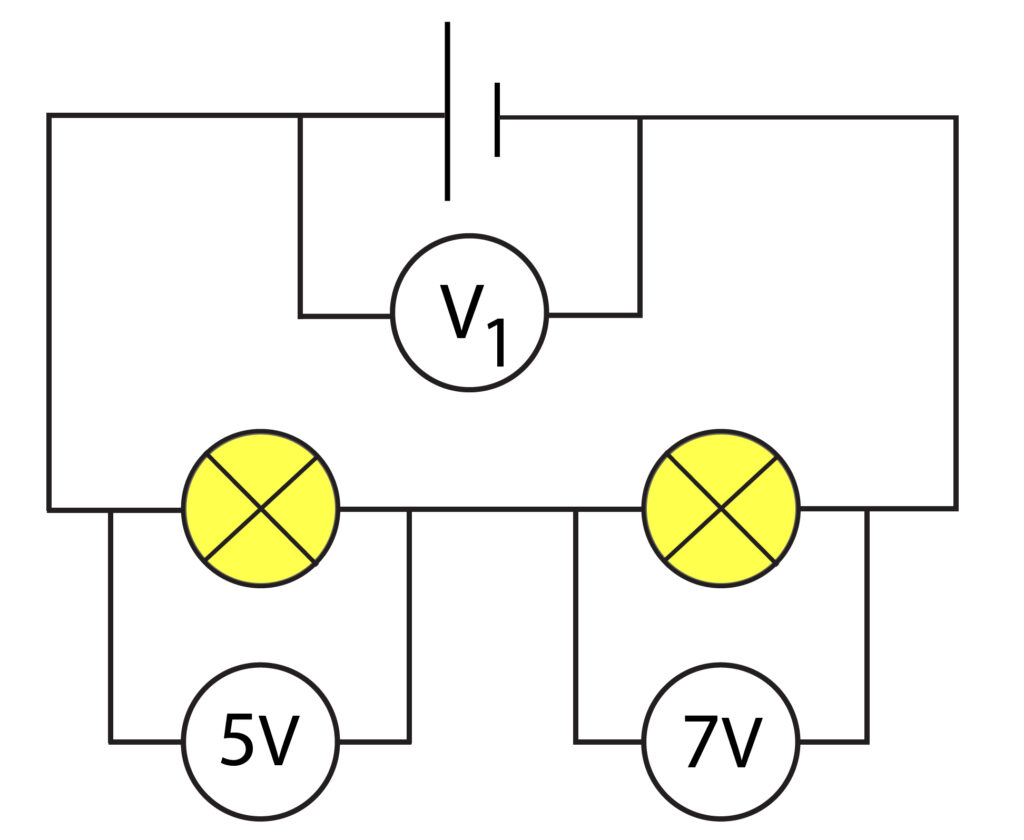
2. Calculate the potential difference across the cell for voltmeter V1, using the cell diagram below.
3. The total resistance of a series circuit is 35 ohms. There are 3 resistors in series, that each have their own resistance value in the ratio of 4:2:1. Calculate the resistance of each resistor.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations