GCSE Resultant Forces
Resultant Forces
A resultant force is a single force that takes account of all the forces acting on an object.
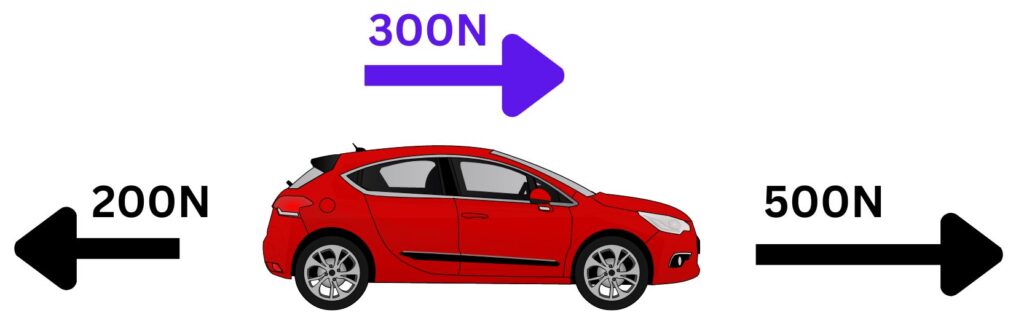
In the diagram above, the car has a forward driving force of 500N, drag forces of 200N.
So, the resultant force is 500N-200N = 300N to the right.
This example can also be represented using a box diagram as shown below:
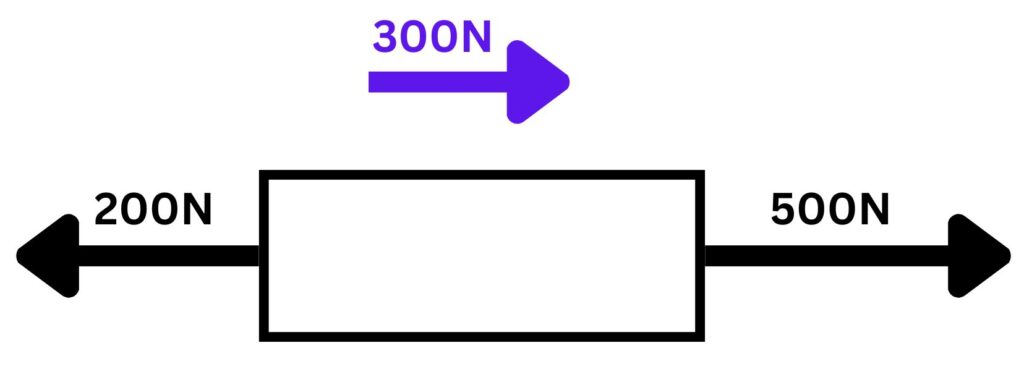
Value of the Resultant Forces
Resultant force of 0N
If the resultant force is 0N, then this means that the forces acting on the object are balanced as shown below.

In this case there is a 500N downwards force due to weight and a 500N upwards force. These forces are equal in size, but opposite in direction. Therefore, the resultant force is 0N and the forces acting on the object are balanced.
500N-500N = 0N.
Resultant force is not 0N.
Sometimes the forces on an object do not cancel out completely, so there is an overall resultant force. This means that the forces are unbalanced.
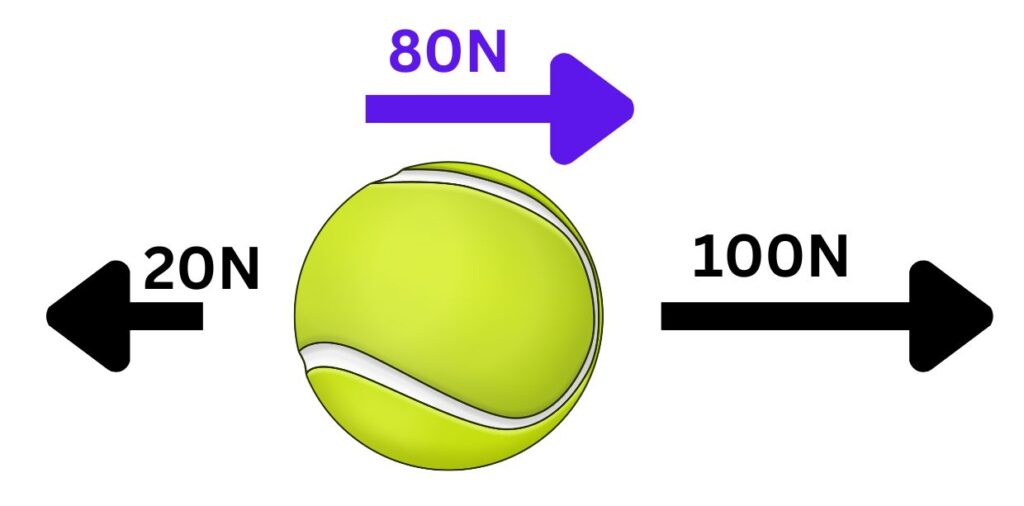
In this case the tennis ball has a forward force of 100N, but drag force of 20N. So, the resultant force is 80N to the right, or in forwards direction.
100N-20N = 80N
Practice Questions
1. Use the following box diagrams to calculate the overall resultant force, in addition state the direction of the resultant force.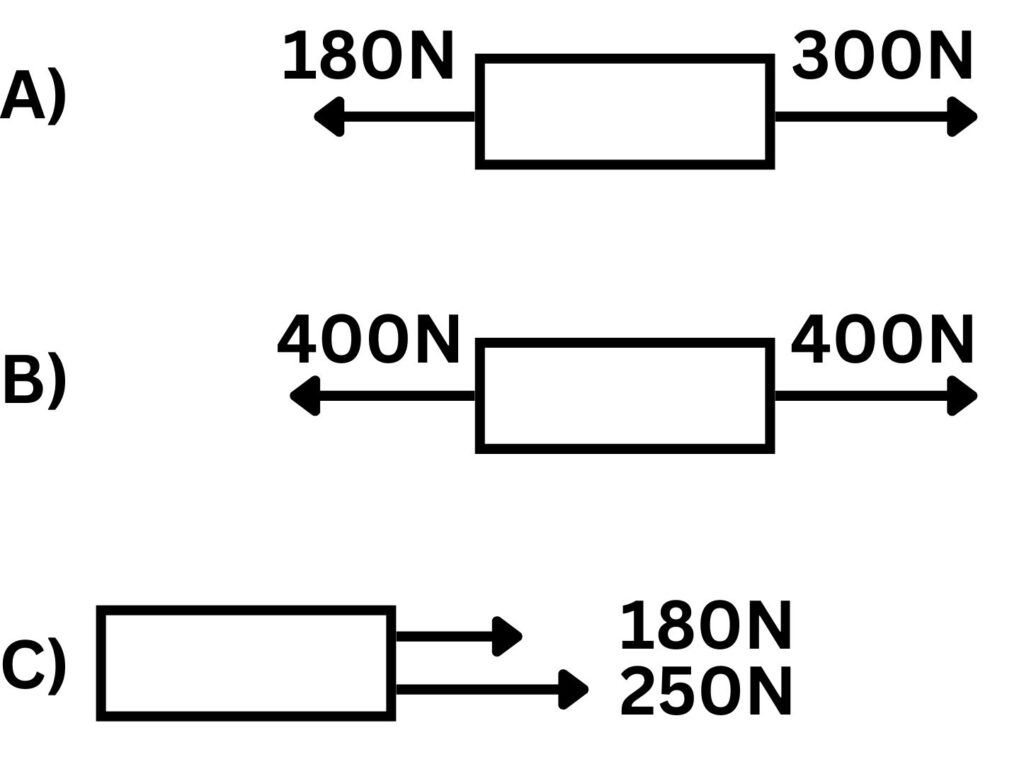
2.A cardboard box is placed onto the floor. Whe box has a weight of 50N and the floor provides a reaction force that is equal in size, but opposite in direction. Draw a box diagram to represent this.
3. An airplane has a engine thrust force of 5kN and air resistance of 2kN. Calculate the resultant force on the airplane.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations