GCSE Random nature of radioactive decay
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive decay is a random process, it cannot be predicted.
It is not possible to predict when an individual nucleus will undergo decay.
However, if you have a large number of nuclei, we can predict how many will decay in a certain time period. This is because we know that after a certain time period, the number of unstable nuclei will halve, due to the half life.
If you take the example of the playing cards, you cannot easily draw an Ace of hearts. However, you do know that every 1 in 4 cards is a heart card. Therefore, if you go through the whole pack of 52 cards, 13 of them will be hearts and one will be the ace of hearts.
 Think of radioactive decay being random a bit like selecting a playing card. The card you receive is random, radioactive decay is similar.
Think of radioactive decay being random a bit like selecting a playing card. The card you receive is random, radioactive decay is similar.
It is not possible to speed the process up, or slow it down. This makes radioactive decay different to a chemical reaction.
Measuring the random nature of decay
The count rate detected by the GM tube varies continuously as shown by the graph. Sometimes the activity is higher and other times lower.
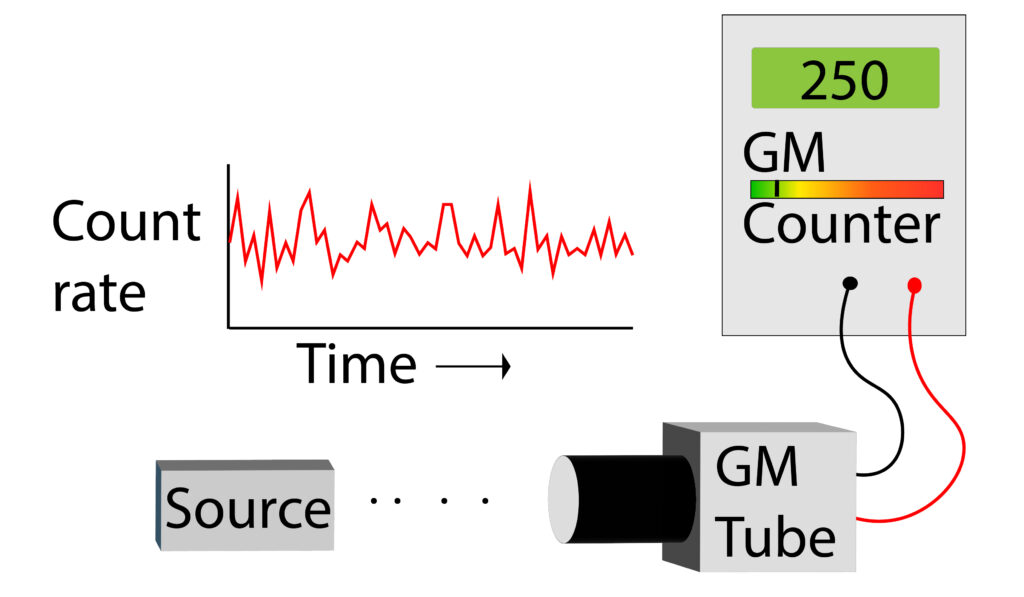
In the case of the graph here, the count rate of the source was measured over a short period of time, just to show the random nature of decay.
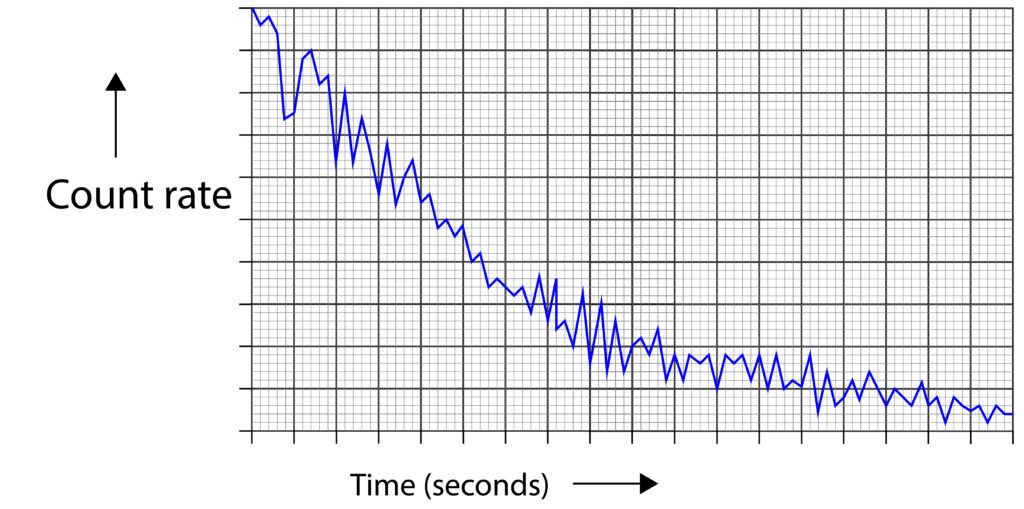
If the source is measured over a longer period of time, it will slowly decay, so the activity would decrease, but it would still show random fluctuations in the activity level
Practice Questions
1.Explain why it is not possible to predict the count rate of a sample of radioactive isotope.
2. A student asked his teacher, if you heat a radioactive substance will it decay faster? Suggest the teacher’s response to the student’s question.
3. Which piece of apparatus can you use to measure the count rate of a radioactive substance?
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations