GCSE Power
Power is the rate of energy transfer.
It is a measure of how quickly energy can be transferred from one energy store to another.
There are two equations that you need to know,

Power is measured in Watts, W. It can also be measured in Joules per second, J/s. However, the standard in GCSE is Watts,W.
1 Watt = 1 Joule per second.
Work done, means energy transferred and is measured in Joules.
Time taken is measured in seconds.
Remember to convert your units before using the equation
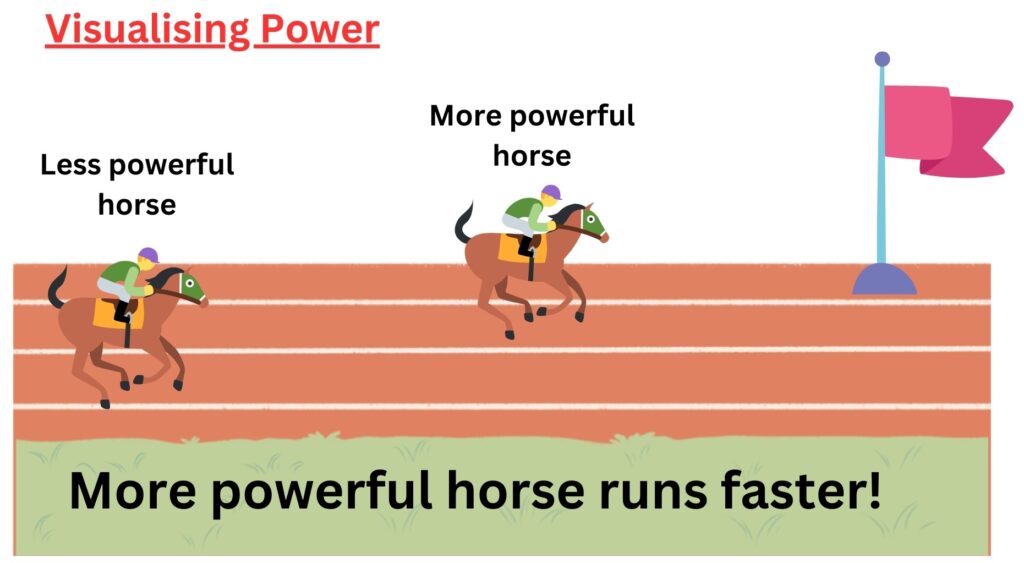
Visualising Power
In the diagram below, both horses do the same amount of work, or transfer the same amount of energy mechanically from their chemical energy store to kinetic energy store.
However the horse on the right, transfers the energy is a shorter time period, so it runs faster.
Just one more point, if the track were long enough, both horses would reach the same maximum speed, but the lower power horse would take longer to reach the maximum speed.
Practice Questions
1. An electric motor transfers 1200J in 4 seconds. Calculate the power of the electric motor .
2. A light bulb will transfer 12000J of energy over a period of 5 minutes. Calculate the power.
3. There are two electric drills in the shop. Drill A will transfer 25kJ of energy in 3 minutes. Whilst drill B will transfer 20kJ of energy over 4 minutes. Which drill A or B is the most powerful?
4.An electric shower has a power rating of 8kW and is used for 5 minutes, 3 times a day, for 1 week. Calculate the total energy transferred.
Need more questions, try our worksheets.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations