GCSE Nuclear Power
Nuclear power
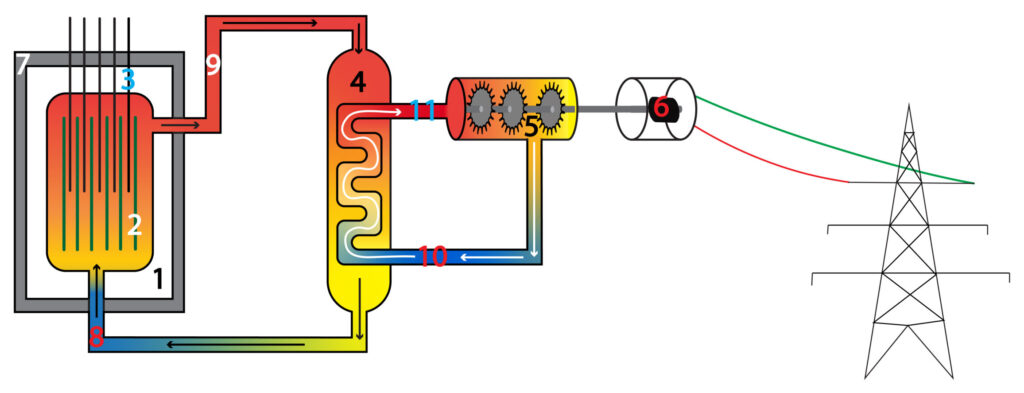
1.Nuclear Reactor
2. Fuel rod
3. Control rod
4. Heat exchanger
5.Steam turbine
6. Generator
7. Concrete shield
8. Cool water entering reactor
9. Steam leaving reactor and entering heat exchanger
10. Cooler water leaving steam turbine and entering heat exchanger.
11. Steam leaving heat exchanger and entering steam turbine
Nuclear fission occurs in the reactor, causing nuclear energy store in the atoms of the fuel rods to be transferred by heating to the thermal energy store of water that enters the reactor. Water in the reactor gains thermal energy and becomes steam, entering the heat exchanger.
In the heat exchanger the steam that has entered from the reactor will transfer energy by heating from its thermal energy store to the thermal energy store of water in the pipe. Water in the pipe gains thermal energy and forms steam.
Steam in the pipe enters the steam turbine and transfers its thermal energy store to the kinetic energy store of the turbine mechanically, causing the turbine blades to rotate.
The kinetic energy store of turbine blades is transferred mechanically to the kinetic energy store of the generator to produce electricity.
The electricity can be used for:
Heating of homes with electric heaters
Transportation (electric vehicles)
Electrical appliances
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| High energy density | Risk of nuclear accident and explosion |
| No carbon dioxide produced | Radioactive waste stays radioactive for a long time |
| Does not contribute to global warming | Expensive to build and decommission |
| Reliable, energy can be generated constantly | Long start up time, so cannot quickly respond to changes in demand |
Practice Questions
1. Many people object if there is a proposed nuclear power station to be built in their local area. Suggest three reasons for their objection
2. Suggest how the use of nuclear power is better for the environment compared to burning of fossil fuels
3. What are the advantages of using nuclear power over renewable energy resources such as wind and solar?
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations