GCSE Measuring Radiation from Radioactivity
Measuring Radiation from Radioactivity
Detecting Radiation
Radiation can be detected using photographic film. When photographic film is exposed to radiation it will turn foggy or darken.
Activity
Definition of activity:
Activity is the rate at which a source of unstable nuclei decays.
A source is any radioactive substance that contains unstable nuclei.
Different isotopes will decay a different rates, so they will have different levels of activity.
Activity is measured in becquerel (Bq)
The faster the rate of decay, greater the activity and greater the number of becquerels
1 Bq means one nucleus decays per second.
If a source has an activity of 500Bq, over 30 seconds there would be
500 Bq x 30 seconds = 15,000 nuclei decay
Geiger Counter
A Geiger Muller tube can detect radiation and is connected to a Geiger muller counter to measure the number of decays per second.

Count-rate is the number of decays recorded each second by a detector.
A geiger counter detects 2000 counts over 15 minutes. Calculate the number of counts per second.
In 15 minutes there are (15 x 60 = 900 seconds)
2000/900 = 2.22 counts per second
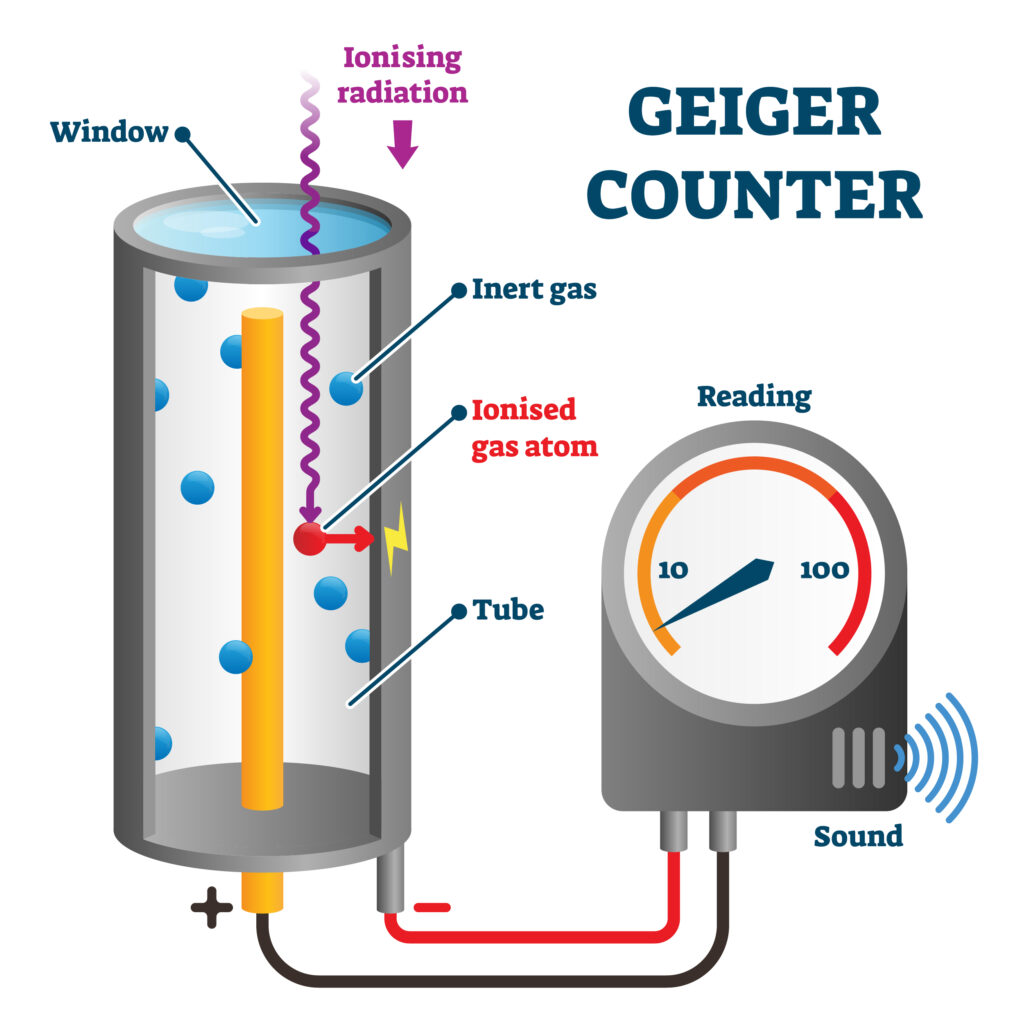
Ionising radiation enters the GM tube, ionises gas molecules or atoms to form ions. This set up an electrical current and the size of the current indicates the count rate. (How the Geiger Counter works is not currently needed on AQA, the information here is for background information only)
Difference between Activity and Count Rate
Activity is the rate at which a source of unstable nuclei decays.
Count-rate is the number of decays recorded each second by a detector.
This means that activity and count rate can be different. If the Geiger counter does not record all of the decays then the count rate will be less than the activity of the source
Practice Questions
1.State two ways that radiation can be detected
2. Define the term activity
3. Explain the meaning of the unit Becquerel
4. A source has an activity of 7500Bq. Calculate how many nuclei decay over 2 minutes.
5. A geiger counter records an average count rate of 3.5 counts per second. Calculate the count rate per minute.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations