GCSE Mass number and Atomic Number
Mass Number and Atomic Number
The periodic table lists the elements, each element has a symbol with two numbers. One number is above the symbol and the other number is below the symbol.
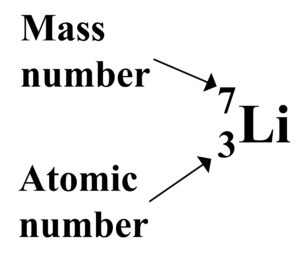
The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons
The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom of the element. All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons.
Number of Neutrons = Mass number – Atomic number.
Overall charge of an atom
Atoms have no overall electrical charge.
Each proton has a +1 charge and each electron a -1 charge.
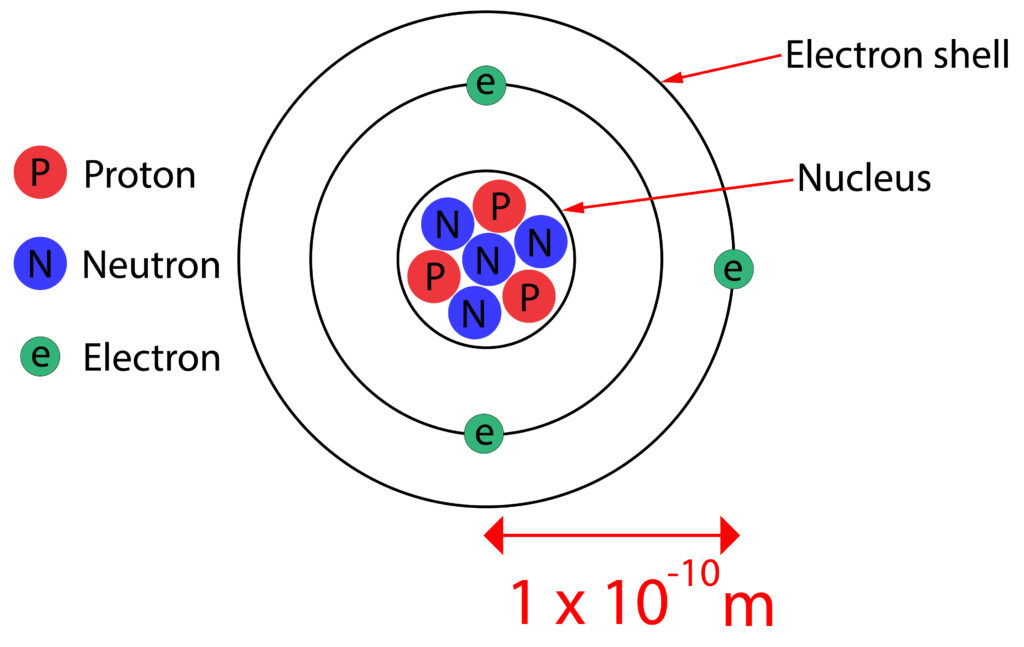
In a neutral atom the number of electrons in an atom is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus
Practice Questions
1. Using a periodic table, write down the mass number and atomic number of Fluorine.
If you do not have access to a periodic table, you can use the AQA one here
2. How many neutrons are in an atom of Phosphorous-31?
3. Explain why Aluminium atoms are electrically neutral
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations