GCSE Linear and non linear force-extension graphs
Linear force-extension graphs
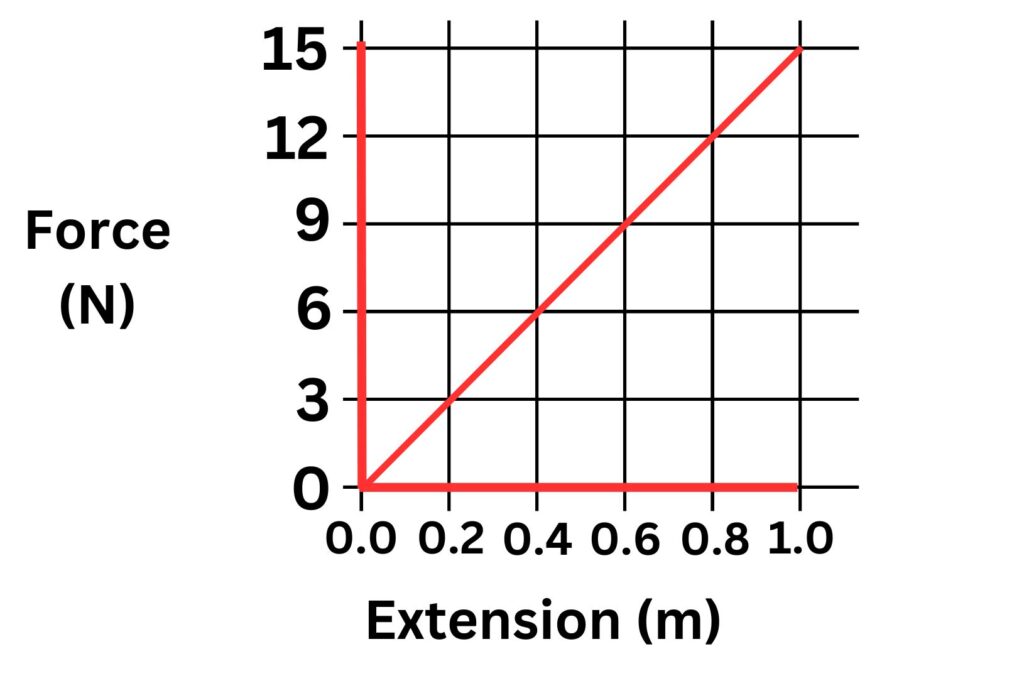
A linear Force extension graph is one that will obey Hooke’s Law.
Hooke’s law states that:
The extension of an elastic object, is directly proportional to the force applied, provided that the limit of proportionality is not exceeded.
An example of a linear force extension graph is shown below:
Non linear Force-extension graph
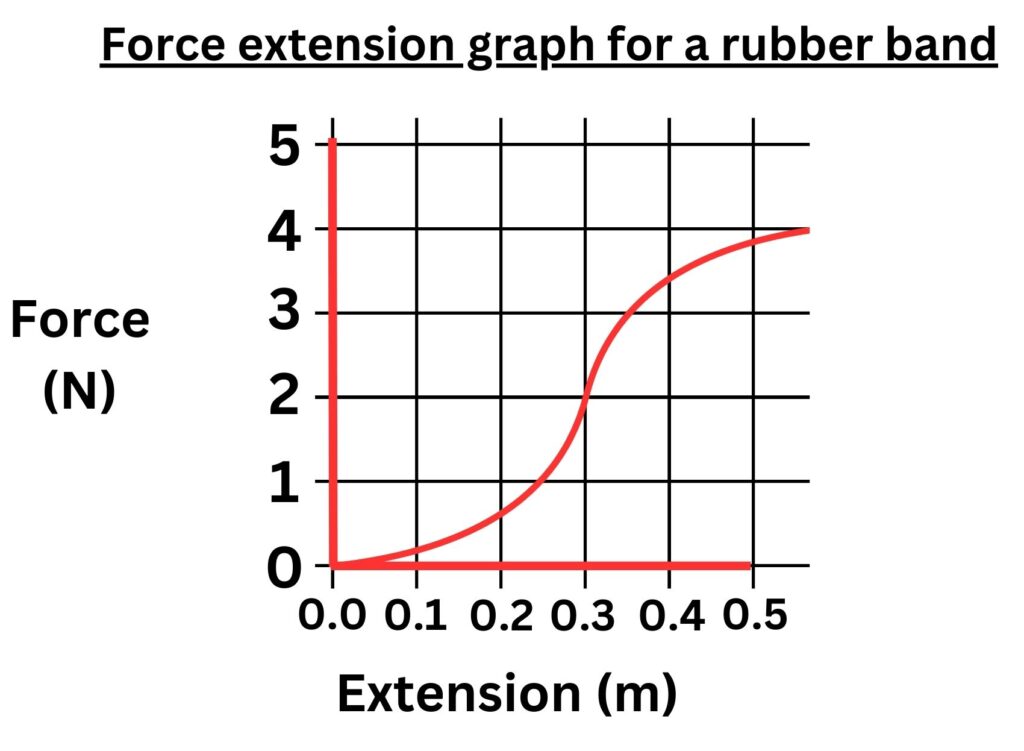
A non linear force extension graph will not follow Hooke’s law. This means that the graph line will be curved and not straight.
An example of a non linear force extension graph is shown below:
Practice Questions
1.Describe the difference between a force extension graph that is linear, vs one that is non linear.
2.Is the following graph representative of linear or non linear?
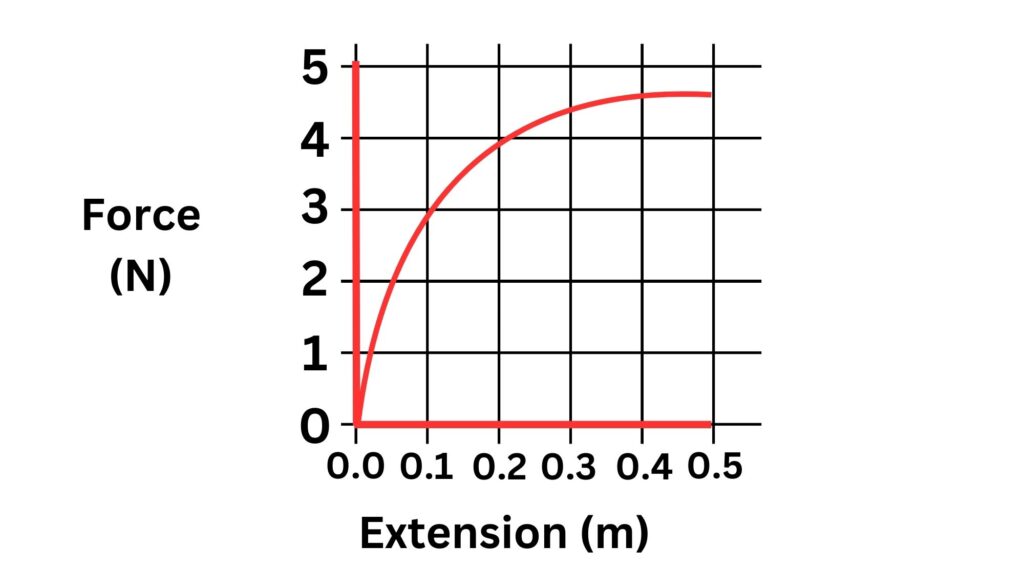
3. Would the following data produce a graph that is linear or non linear?
| Mass added to spring (kg) | Force, F(N) | Extension, e (m) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 1 | 0.05 |
| 0.2 | 2 | 0.10 |
| 0.3 | 3 | 0.15 |
| 0.4 | 4 | 0.20 |
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations