GCSE Electrical Power
Electrical Power
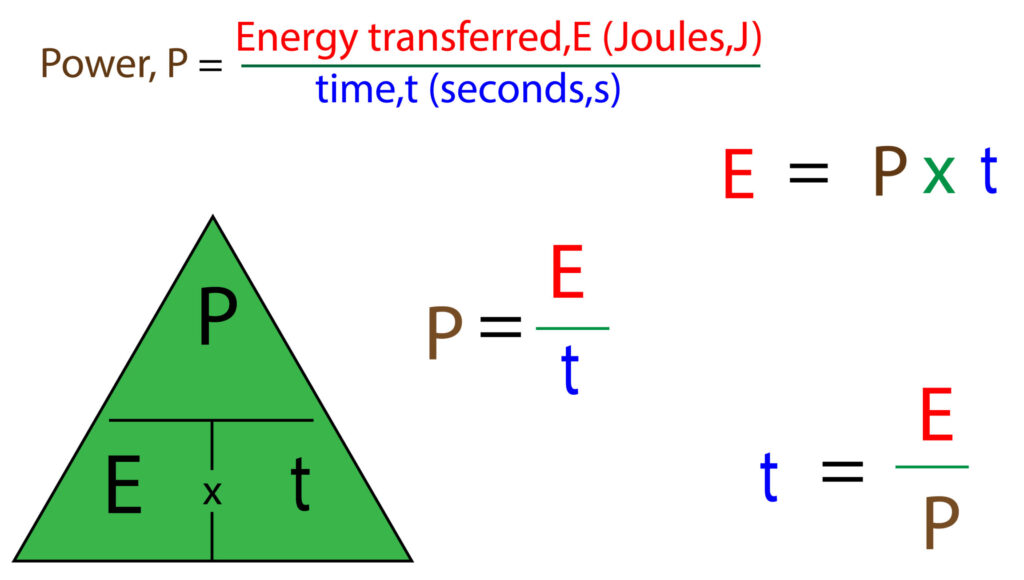
Electrical power is the rate of energy transfer.
There are different equations for working with electrical power
Example question
A 5W light bulb is switched on for 2 minutes, calculate the energy transferred.
Convert the 2 minutes into seconds. 2 minutes = 120 seconds
Energy = Power x time
Energy = 5W x 120 seconds
Energy = 600J
Example calculation
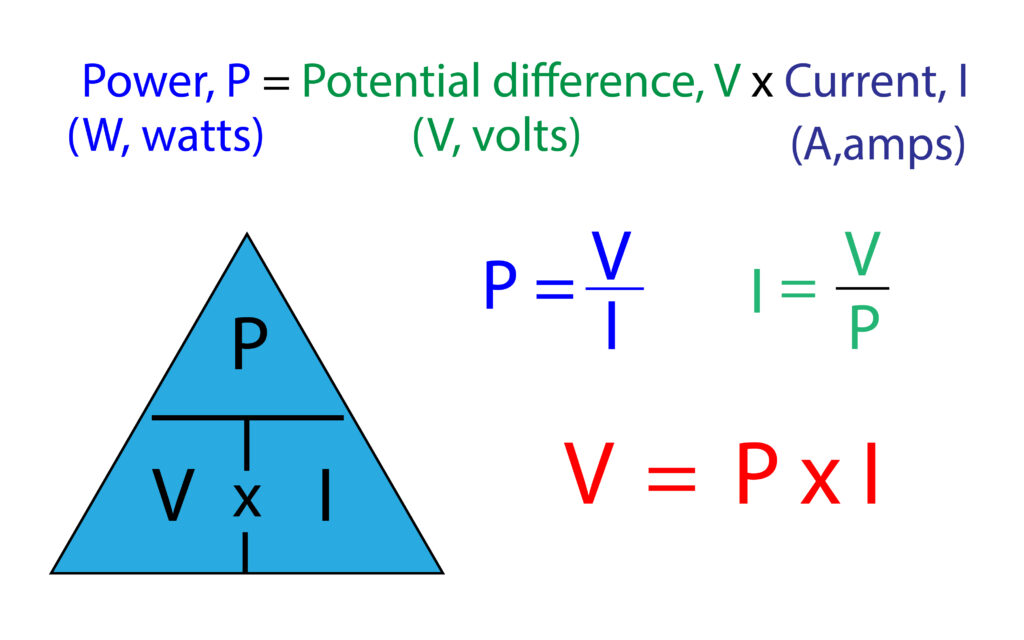
1. A mains kettle uses 2300W and 230V.
(a)Calculate the current that kettle uses for normal use.
P = V x I
I = P/V
I = 2300/230 = 10A
Example calculation
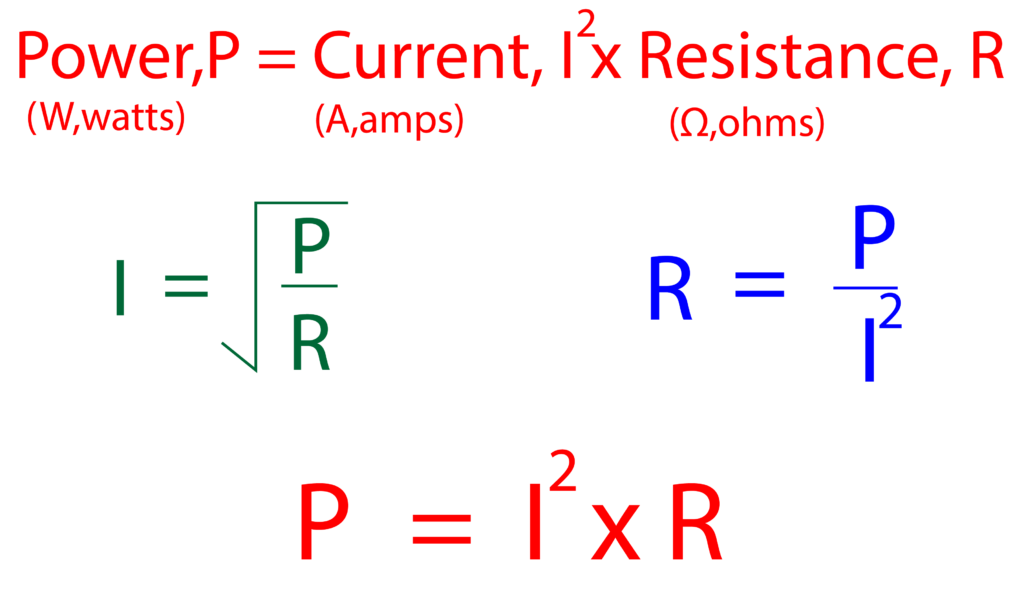
1. A tumble dryer has a current of 11A flowing and a resistance of 20 ohms. Calculate the power of the tumble dryer.
P = I2 x R
P = 112 x 20
P = 2420W
Practice Questions
1.An electric heater uses 12.9kJ of energy whilst switched onand has a power rating of 600W. Calculate how long the heater was switched on for.
2.A 3kW kettle draw a current of 12A from the mains supply. Calculate the potential difference of the mains supply
3.A dishwasher has a power rating of 1.2kW and a resistance of 40Ω. Calculate the current flowing through the dishwasher.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations