GCSE Electric Fields and Objects
Electric Field.
An electric field will occur around a charged object. See the diagram below.
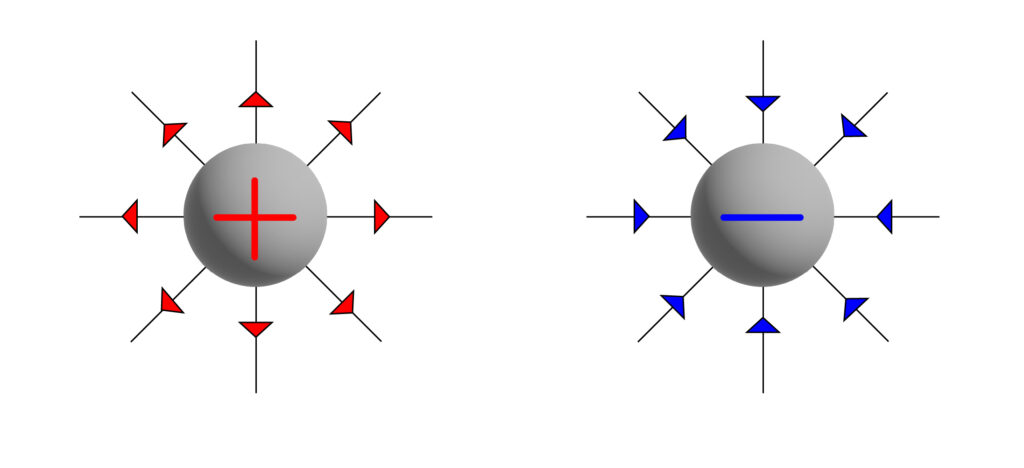
The lines around the spheres, show lines of force. On the positive sphere the lines of force point away from the sphere, whilst on negative sphere lines of force point towards the sphere
Electric Fields and Charged objects.
If a charged object is in an electric field, it will experience an electrostatic force, this is a non contact force.
Oppositely charged objects next to each other.
If both of the charged spheres above are placed next to each other, then the electric fields interact as show below:
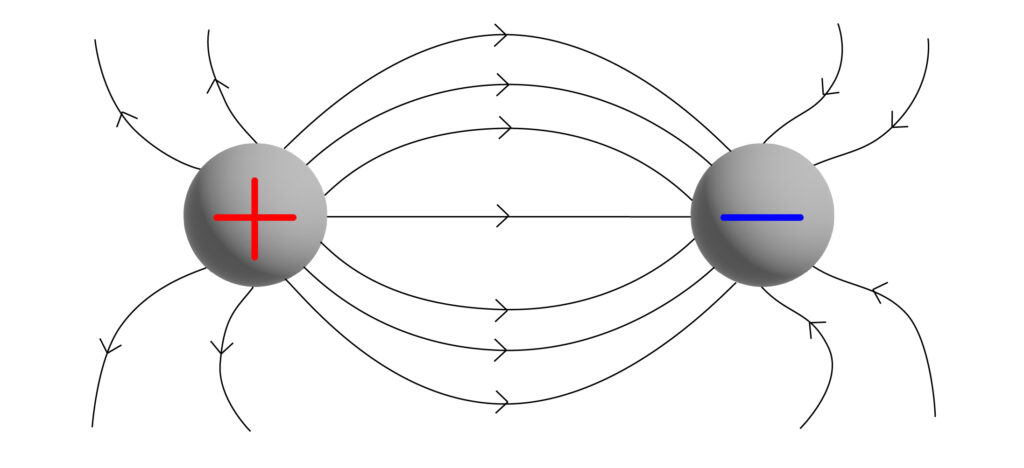
(This diagram is not on AQA GCSE, it is only here to help your understanding of the topic)
It is possible for an electric spark to occur between the oppositely charged objects, due to the electric field present. A spark occurs if the electric field strength becomes high enough to ionise the surrounding medium, typically air. This ionisation creates a conductive path for the electric charge to flow, resulting in a spark.
As both, the object and sphere have opposite charges then a force of attraction occurs as shown below:
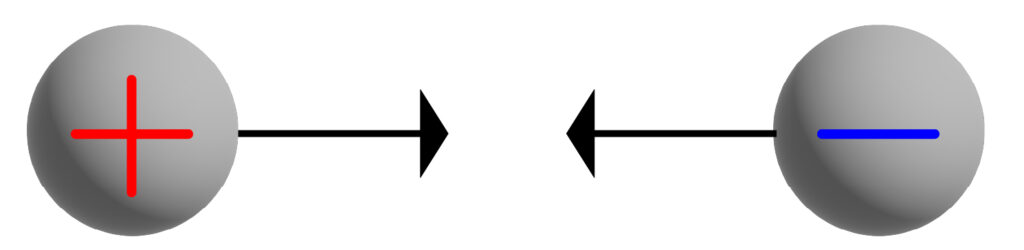
The field lines have been removed to make the diagram easier to understand, although they would still be present in real life!
The diagram directly above you will need for your course!
Objects with like charges next to each other.
When objects with like charges are brought close the electric fields interact as shown below:
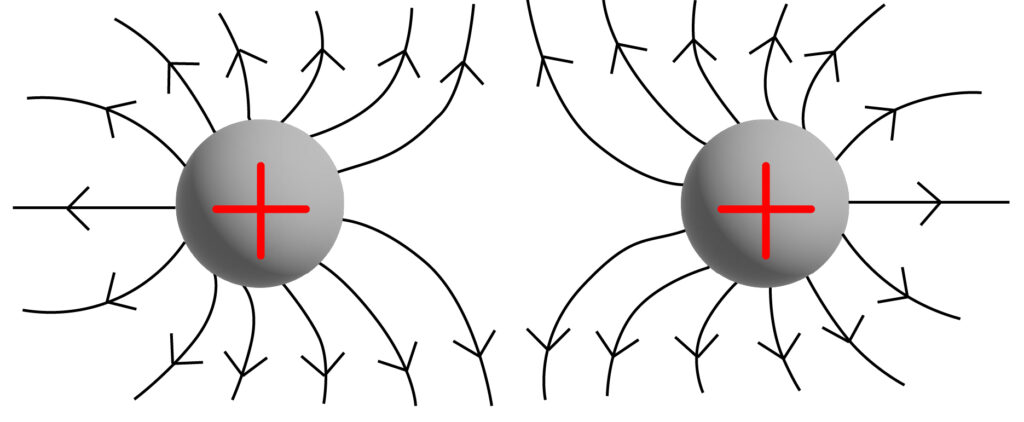
(This diagram is not on AQA GCSE, it is only here to help your understanding of the topic)
It is possible for an electric spark to occur between the two like charged objects, due to the electric field present. A spark occurs if the electric field strength becomes high enough to ionise the surrounding medium, typically air. This ionisation creates a conductive path for the electric charge to flow, resulting in a spark.
The objects experience a force and repel each other.

Again in the diagram above the lines of force have been removed for simplification, so that you can see the force arrows clearly.
The diagram directly above you will need for your course!
The effect of distance on the force.
Remember every charged object has an electric field around itself.
When two charged objects are near each other, their electric fields interact.
Both objects experience a force. The closer the objects the greater the forces involved.
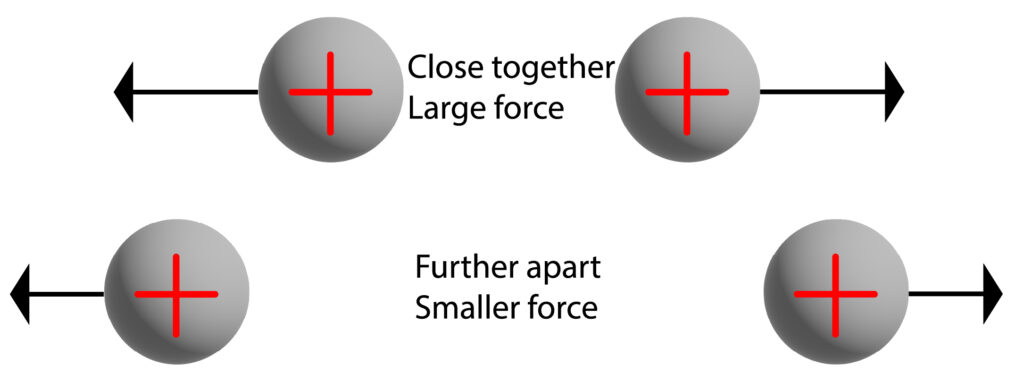
In the diagram above the electric fields have been hidden to make the diagram clearer and easier to understand. Only the force arrows are visible.
Practice Questions
1. Describe how an electric field is formed
2. Explain what happens when a negatively charged object is placed into an electric field being generated by a positively charged object
3. Explain what happens when a positively charged object is placed into an electric field being generated by a positively charged object
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations