GCSE Efficiency
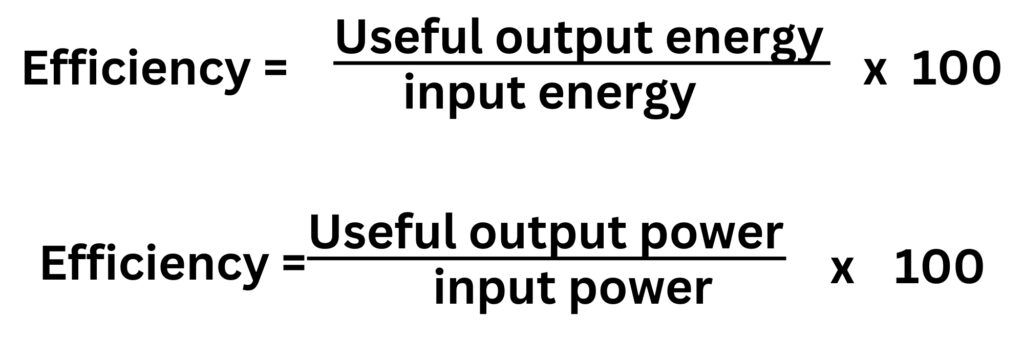
Efficiency
Efficiency is a measure of how much of the input energy is transferred into useful output energy, or how much of the input power is transferred into useful output power.
Efficiency and Sankey Diagrams
You may have to draw, or interpret sankey diagrams.
Here is a guide to Sankey diagrams:
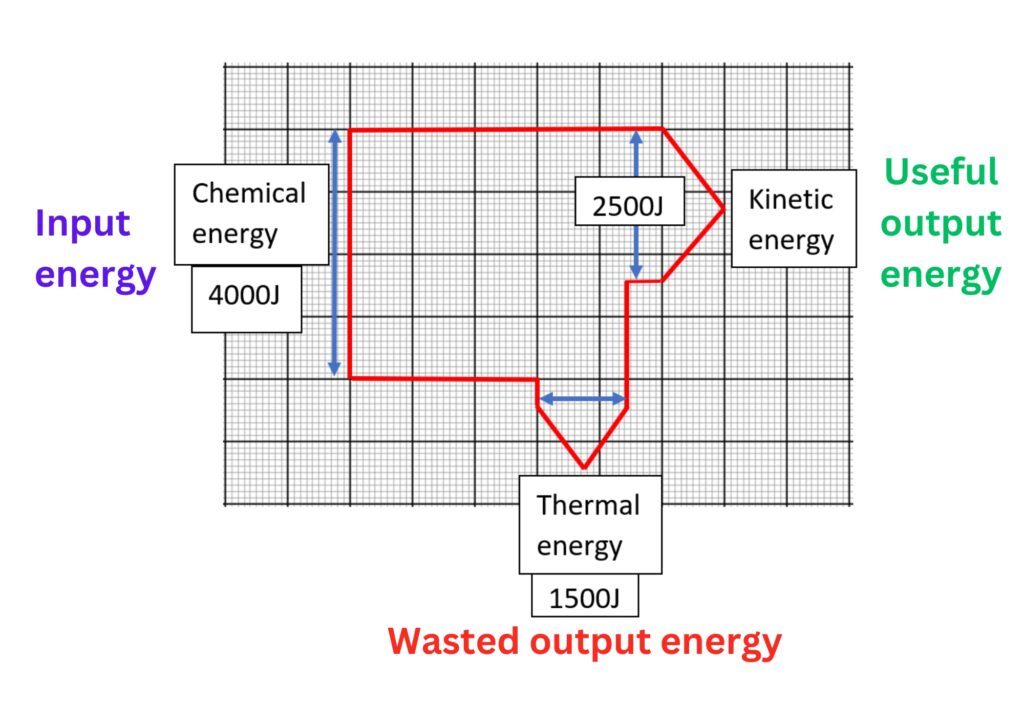
The diagram is drawn to scale.
On the left is the input energy (4000J). Arrow is vertical, every tiny box is worth 100J, count along the arrow 40 boxes, so 4000J.
On the right is the useful energy outputs (2500J). Arrow is vertical, 25 tiny boxes along arrow, each box 100J, so 2500J.
On the bottom is the wasted energy outputs. (1500J). Arrow is horizontal, count tiny boxes along arrow, 15 boxes so 1500J.
Practice Questions
1.The electric motor in a fan will transfer 300J of chemical energy mechanically to 225J of kinetic energy, the remaining 75J of energy is transferred by radiation to the thermal energy store of the surroundings. Calculate the efficiency of the fan.
2. A wind turbine will transfer 1.0 x 106J of kinetic energy electrically into 600,000J of chemical energy to charge up a battery. The remaining energy is transferred by radiation to the thermal energy store of the surroundings.
Calculate the efficiency of the wind turbine.
3. The energy used to increase the temperature of 1kg of water in a kettle is 2 x 106J. The kettle has a rated efficiency of 80%. Calculate the input energy that the kettle requires.
4. An electric motor uses a power of 150W to raise an object in height. 100J of work is done on the object over 0.8 seconds. Calculate the efficiency of the electric motor.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations