GCSE Atomic Structure
Atomic Structure
All substances are made up of atoms. Atoms have a radius of about 1 x 10-10m
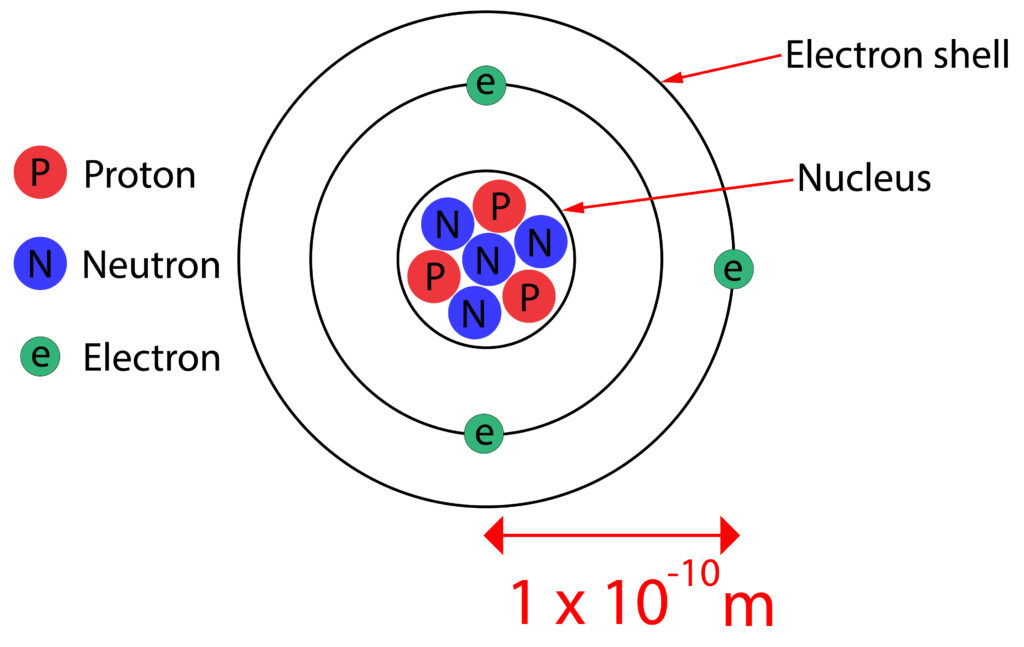
The nucleus of the atom is 1/10000th the size of the whole atom, but contains most of the mass.
The nucleus contains protons and neutrons.
Protons have a positive charge, whilst neutrons are neutral, so the nucleus has a positive charge overall.
The negatively charged electrons are found electron shells or energy levels around the nucleus of the atom.
This means that most of the atom is empty space.
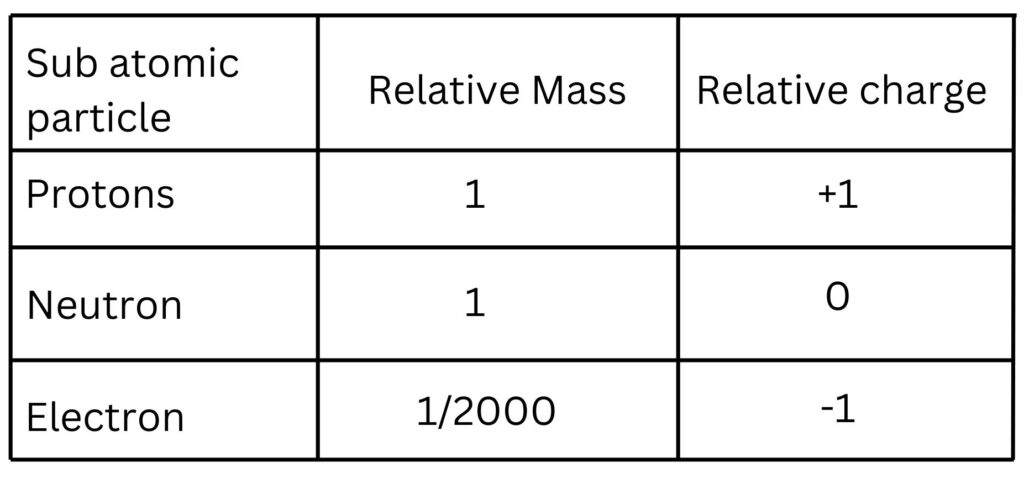
Arranging Electrons in an atom.
Electrons are arranged around the nucleus in energy levels or electron shells.
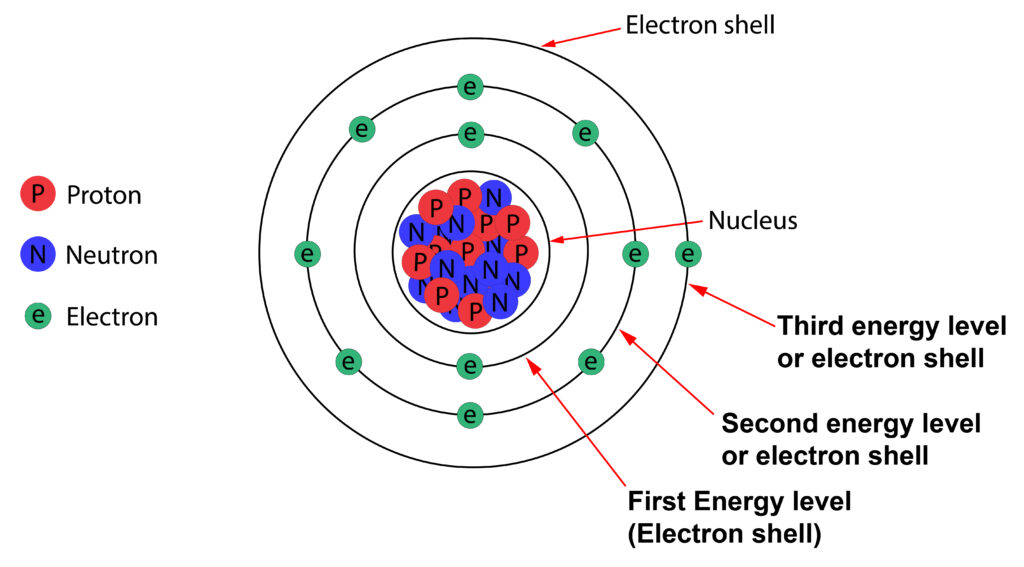
The first energy level can hold up to 2 electrons. The second or third energy level can hold up to 8 electrons.
The second energy level is at a higher energy level than the first energy level. This pattern continues, so the further the energy level is from the nucleus, the greater the energy of the electrons in that energy level.
It is possible for the electrons to move from one energy level to the next, we will explore that idea in the next page of notes.
1. State the names of the three subatomic particles present in and atom.
2. The radius of a typical atom is 1 x 10-10m. Calculate the size of the radius of the nucleus.
3. Calculate the relative mass of the nucleus that is seen in the picture of the atom at the very top of this page.
4.State how many electrons as a maximum should be in the first, second and third energy levels of an atom.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations