GCSE Absorption and Emission of Electromagnetic Radiation
Absorption and Emission of Electromagnetic Radiation
The electrons are in energy levels around the nucleus of the atom.
Low energy levels are close to nucleus
Higher energy levels are further from the nucleus.
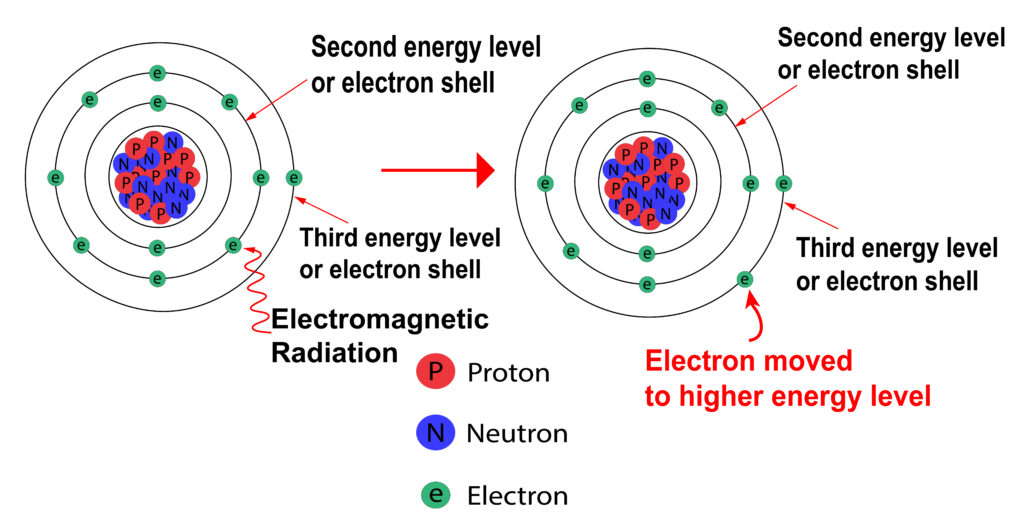
Absorption of Electromagnetic Radiation
When electromagnetic radiation (e.g. Light or Infrared(heat)) is supplied an electron can move from a lower energy level to a higher energy level as shown below.
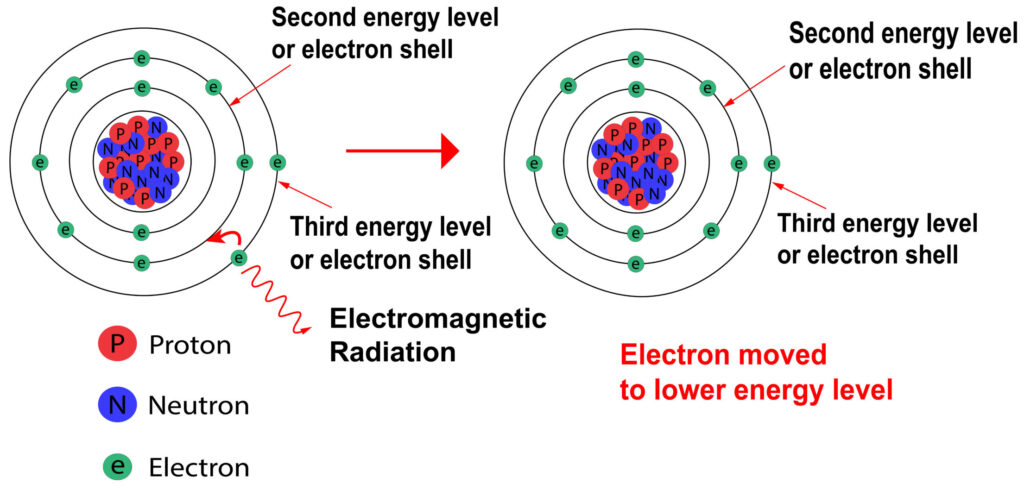
Emission of EM radiation
Electrons in higher energy levels can move to lower energy levels providing that the lower energy level is not full. When the electron moves to the lower energy level, electromagnetic radiation is released.
Real life example
A real life example of the electrons moving between the energy levels happens in a flame test. When a chemical substance is placed into the blue roaring flame of a bunsen burner a colour is seen.

Thermal energy or heat radiation is supplied to the substance, causing electrons to move from lower energy level to higher energy level as the electrons absorb the thermal EM radiation. The electrons will then move back down from high energy level to lower energy level emitting light EM Radiation
Practice Questions
1.When sodium chloride is placed into the blue roaring flame of a bunsen burner state what you would observe
2. Explain the difference between absorption and emission of EM radiation
3. Describe the changes that occurs when an electron is supplied with EM radiation, then later releases that EM radiation in terms of energy levels.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations