Answers to GCSE Resultant Forces
Practice Questions
1. Use the following box diagrams to calculate the overall resultant force, in addition state the direction of the resultant force.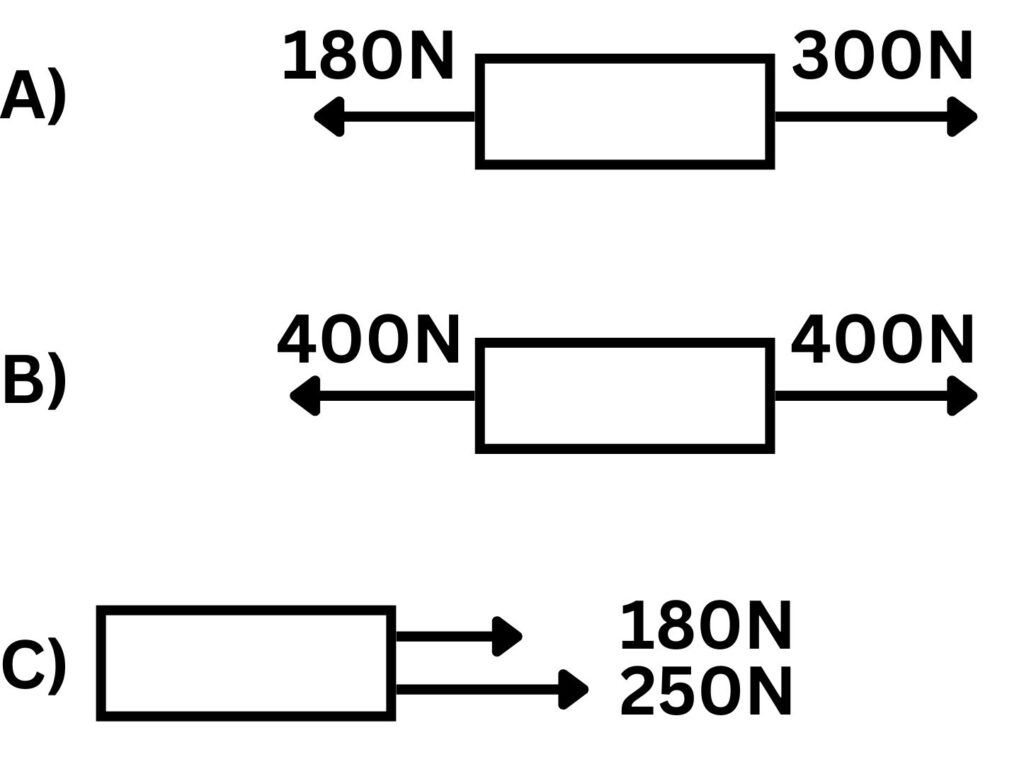
1a) 300N-180N = 120N to the right
1b) 400N-400N = 0N, no direction because the forces cancel
1c) 250N + 180N = 430N to the right
2.A cardboard box is placed onto the floor. Whe box has a weight of 50N and the floor provides a reaction force that is equal in size, but opposite in direction. Draw a box diagram to represent this.
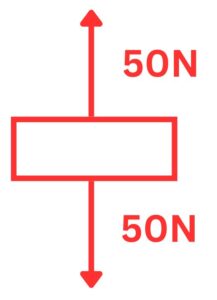
50N – 50N = 0N resultant force
3. An airplane has a engine thrust force of 5kN and air resistance of 2kN. Calculate the resultant force on the airplane.
5kN-2kN = 3kN in the forward direction. 3kN = 3000N
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations