Answers to GCSE Resistors
Practice Questions
1.State Ohm’s Law
Ohm’s law state that the current which flows through a resistor (component) is directly proportional to the potential difference across the resistor, providing that the temperature is constant.
2. Draw a data table to collect the data for the testing resistors experiment above
| Potential difference (V) | Current (A) |
|---|---|
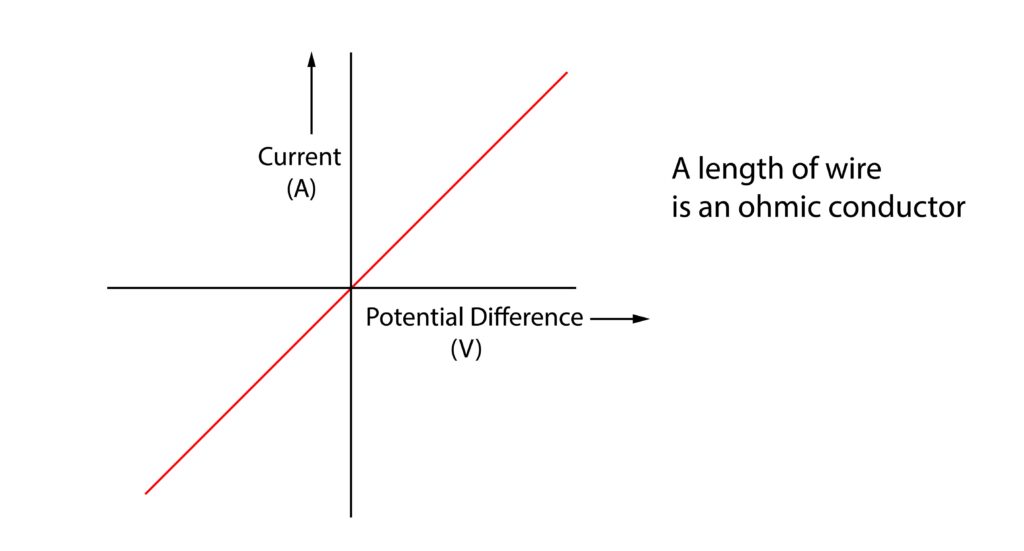
3. Describe and explain the current-potential difference graph for a length of wire.
Starting at 0A, 0V. As the potential difference increases, so does the current, there is a directly proportional relationship. This is consistent with ohms law.
If the terminals are swapped, the same pattern is seen in reverse, this is shown in the bottom left part of the graph.
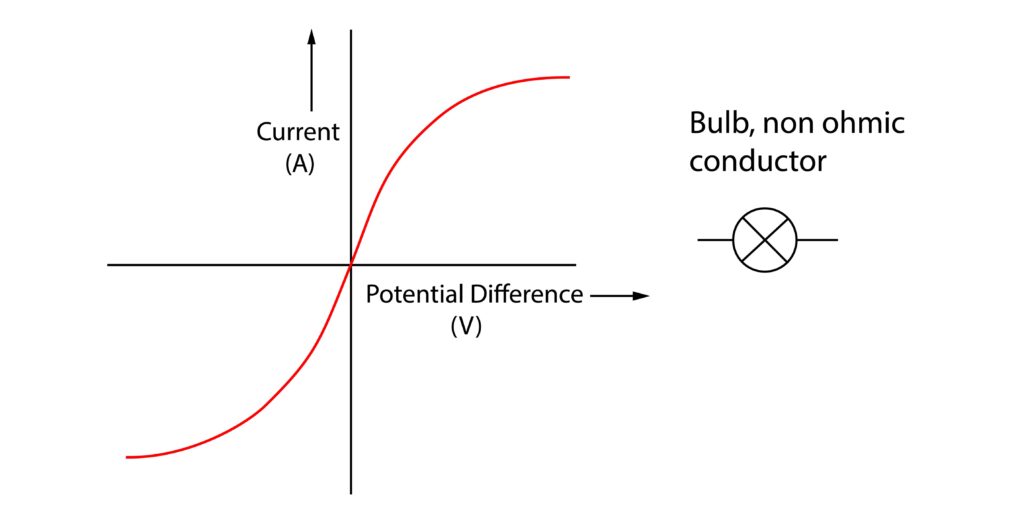
4.Describe and explain the current-potential difference graph for a bulb
Starting at 0A, 0V. As the potential difference increases, the current increases, but reaches a maximum value. This is because the filament wire in the bulb becomes hot and its resistance increases, which limits the current. As a result, this is a non ohmic conductor.
If the terminals are swapped, the same pattern is seen in reverse, this is shown in the bottom left part of the graph.
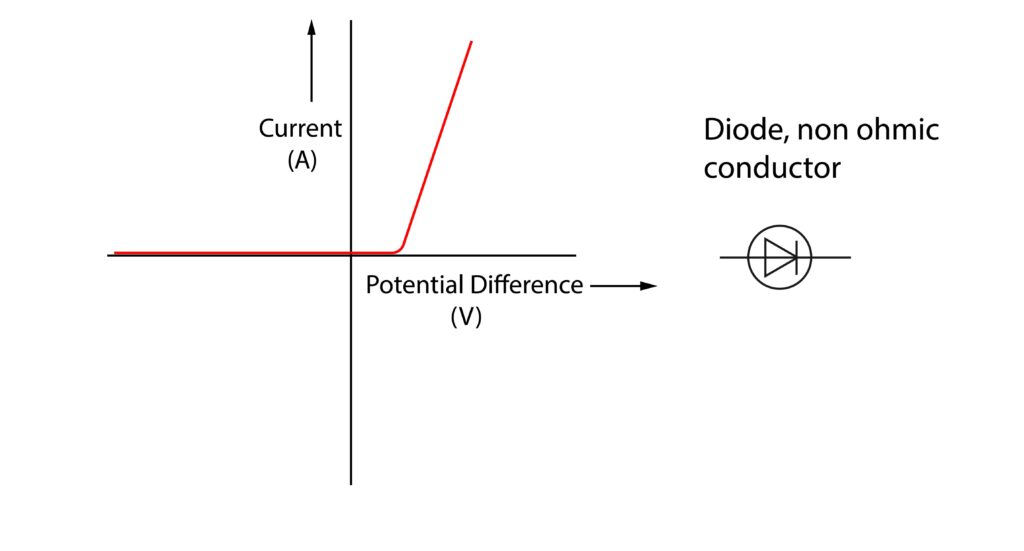
5. Describe and explain the current-potential difference graph for a diode.
A diode has a low resistance direction and a high resistance direction.
Starting at 0A, 0V. As the potential difference increases, at a minimum potential difference in the low resistance direction a current will flow, causing the IV graph to up upwards.
If the terminals are switched so the potential difference would be applied in the high resistance direction for the diode, regardless of the potential difference applied, no current would flow.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations