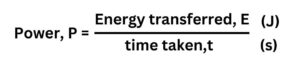
Answers to GCSE Power
Answers to Practice Questions
1.An electric motor transfers 1200J in 4 seconds. Calculate the power of the electric motor.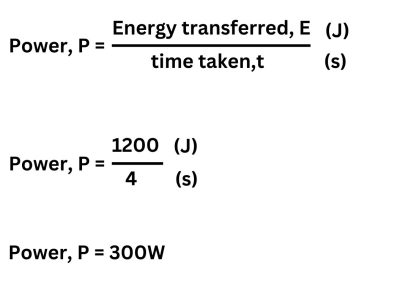
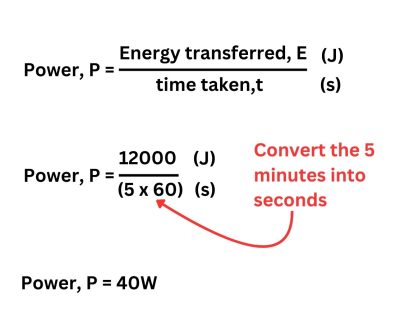
2. A light bulb will transfer 12000J of energy over a period of 5 minutes. Calculate the power.
3. There are two electric drills in the shop. Drill A will transfer 25kJ of energy in 3 minutes. Whilst drill B will transfer 20kJ of energy over 4 minutes. Which drill A or B is the most powerful?
Drill A
25kJ = 25000J
3 minutes ; (3 x 60) = 180 seconds
Drill B
20kJ = 20000J
4 minutes; (4 x 60) = 240 seconds
Power drill A = 25000/180 = 138.9W
Power drill B = 20000/240 = 83.3W
So, drill A is more powerful.
4.An electric shower has a power rating of 8kW and is used for 5 minutes, 3 times a day, for 1 week. Calculate the total energy transferred.
Power = Energy/time
Energy = Power x time
8kW = 8000W
5 minutes; (5 x 60) = 300 seconds
Total time period = 300 x 3 x 7 = 6300 seconds
Need to multiply by 3 because it is used 3 times per day, multiply by 7 as there are 7 days in one week.
Energy used = 8000W x 6300 seconds = 50400000J
or 50400kJ
Need more questions, try our worksheets.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations