Answers to GCSE Latent Heat
Practice Questions
1.State the definition of latent heat
Latent heat is the energy needed to change the state of a substance.
2.Use the graph below to anwer the following question.
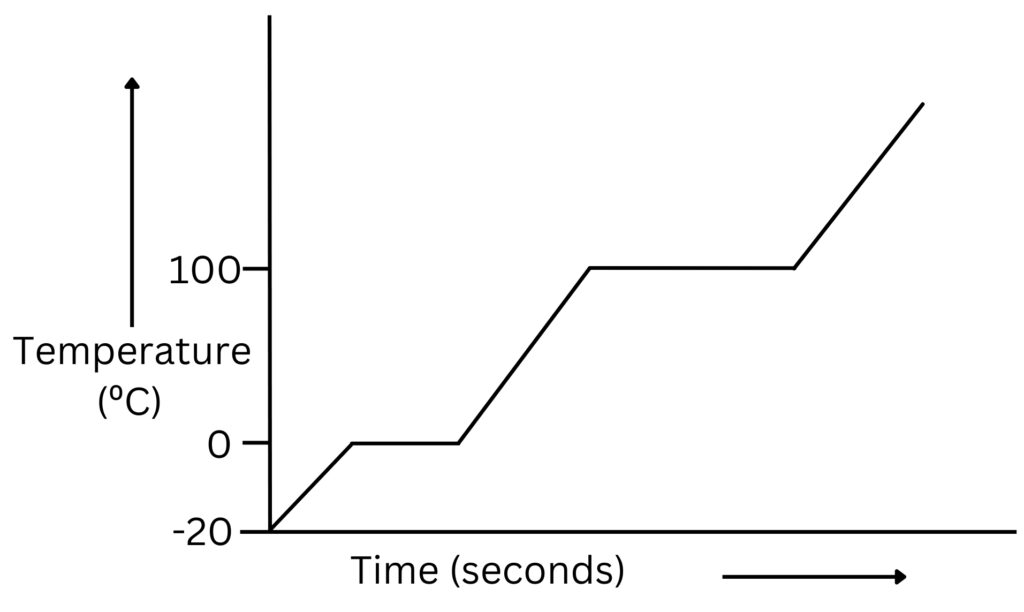
Suggest why the horizontal line for latent heat of vaporisation is longer than the horizontal line for latent heat of fusion
For this substance more energy needs to be supplied for vaporisation compared to fusion. Therefore latent heat of vaporisation is a larger value than latent heat of fusion.
3. Explain how both the intermolecular forces and internal energy of water particles change as steam condenses to form liquid water
As the steam is cooled the internal energy of the water particles will decrease. As the water particles move closer together and decrease in speed, intermolecular forces will form between them as steam condenses to form liquid water.
Absorption and Emission of EM Radiation
JJ Thomson and Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford and the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr changing the Nuclear Model
Discovering the Proton and Neutron
Measuring radiation from radioactivity
Radiation types and properties
Random nature of radioactive decay
Radioactive contamination or irradiation
Hazards of contamination and irradiation
Studies on the effects of radiation on humans
Different half lives of radioactive isotopes
Nuclear Fission Chain Reaction
Writing nuclear fission equations