AQA GCSE Factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis (Biology)
Factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a chemical reaction. Like all reactions, its rate depends on conditions. If one factor is in short supply, it limits the rate.
Rate = how fast photosynthesis happens
The rate can be measured as:
1.Amount of oxygen produced per minute
2. Amount of carbon dioxide used per minute
3. Change in biomass per unit time.
In most cases the amount of oxygen per unit time is measured, either by measuring volume of gas, or by counting bubbles of gas.
Limiting Factors
A limiting factor is a factor that if increased will increase the rate of photosynthesis.
This means:
A limiting factor is the factor in shortest supply.
Increasing the limiting factor increases the rate until something else becomes the limiting factor.
There are four limiting factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis:
1.Temperature
2.Light intensity
3.Carbon dioxide concentration
4.Amount of chlorophyll.
Temperature
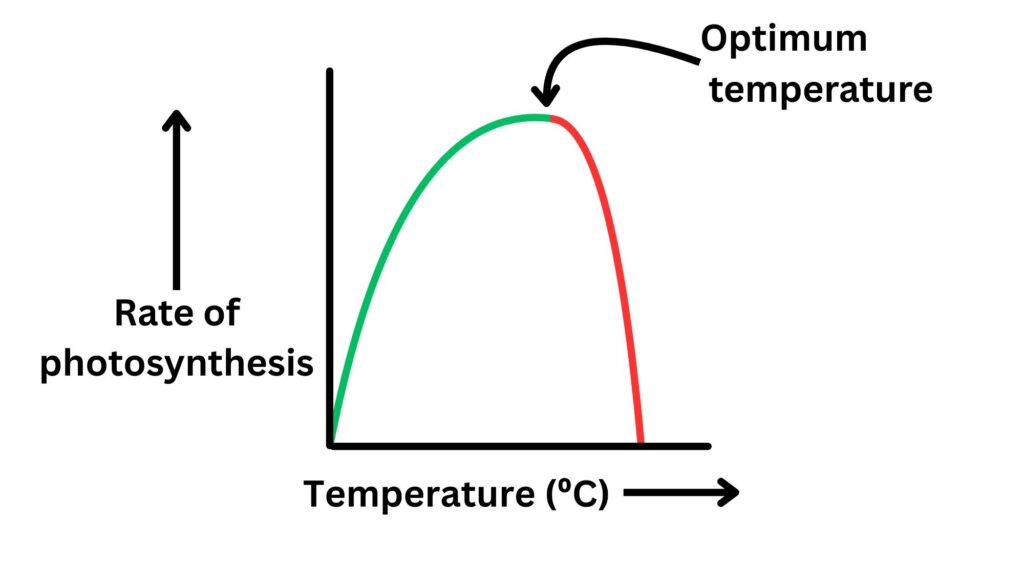
As temperature increases, rate of photosynthesis increases to a maximum, then decreases.
The process of photosynthesis uses enzymes to speed up the reaction.
This trend is shown in the graph below, lets describe and explain it.
Green part of graph:
As temperature increases rate of photosynthesis will increase.
This is because at higher temperatures the particles have more kinetic energy, so the particles move faster, there are more collisions per unit time between the substrates and the enzymes.
During the green part of the graph, temperature would be a limiting factor.
Optimum temperature
The optimum temperature is where the maximum rate for photosynthesis occurs. On our graph, this is where the green line meets the red line.
Red part of the graph:
Beyond the optimum temperature, as temperature is increased then the rate of photosynthesis decreases.
This is because the enzymes that carry out photosynthesis become denatured. This means that the shape of the enzyme’s active site changes and the substrate can no longer bind to the active site, so the reaction rate will decrease to zero.
Light intensity
Overall: As light intensity increases, the rate of photosynthesis increases until it reaches a maximum value.
This is because light provides the energy needed for photosynthesis, and chlorophyll absorbs this light energy. Increasing light intensity increases the amount of energy absorbed, so the rate increases. See the green part of the graph.
At high light intensities, all the chlorophyll is already absorbing light at its maximum rate, so increasing light intensity further has no effect. Light is no longer the limiting factor and another factor becomes limiting, such as carbon dioxide concentration. See the red part of the graph.

Carbon dioxide concentration
Overall:
As carbon dioxide concentration increases, the rate of photosynthesis increases until it reaches a maximum value.
This is because carbon dioxide is a raw material for photosynthesis. Increasing carbon dioxide concentration increases the frequency of successful reactions, so the rate of photosynthesis increases.
Green part of the graph:
As carbon dioxide concentration increases, the rate of photosynthesis increases because carbon dioxide is the limiting factor. There is not enough carbon dioxide for photosynthesis to occur at a faster rate, so increasing its concentration increases the rate.
Red part of the graph:
At higher carbon dioxide concentrations, the rate of photosynthesis becomes constant. This shows that carbon dioxide is no longer the limiting factor. Another factor, such as light intensity, temperature, or the amount of chlorophyll, is now limiting the rate of photosynthesis.

Amount of chlorophyll
As the amount of chlorophyll increases, the rate of photosynthesis increases until it reaches a maximum value.
This is because chlorophyll absorbs light energy needed for photosynthesis. Increasing the amount of chlorophyll increases the amount of light that can be absorbed, so the rate of photosynthesis increases.
Green part of the graph:
At low amounts of chlorophyll, the rate of photosynthesis is low because there is not enough chlorophyll to absorb light energy. During the green part of the graph, the amount of chlorophyll is the limiting factor.
Red part of the graph:
At higher amounts of chlorophyll, the rate of photosynthesis becomes constant. This shows that the amount of chlorophyll is no longer the limiting factor. Even though there is more chlorophyll present, another factor, such as light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, or temperature, is now limiting the rate of photosynthesis.

Practice Questions
1.List three ways the rate of photosynthesis can be measured
2.A plant is kept in low light but high carbon dioxide and optimal temperature. Which factor is limiting photosynthesis and why?
3.During a sunny day, a plant shows no further increase in photosynthesis despite more sunlight. Suggest possible limiting factors.
Factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis
Measuring & calculating rates of photosynthesis
Inverse square law and photosynthesis
Economics of enhancing the conditions in greenhouses
Investigating the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis