AQA GCSE Communicable disease (Biology)
Communicable disease
A communicable disease is an infectious disease spread between organisms and it is caused by pathogens.
Pathogens are microorganisms that cause infectious disease. They can infect both plants and animals.
Examples of pathogens include
1.Bacteria
2.Viruses
3.Fungi
4.Protists.
| Pathogen | How the pathogen makes us ill | Appearance |
|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | Bacteria may produce poisons (toxins) that damage tissues and make us feel ill. Bacteria reproduce rapidly inside the body | 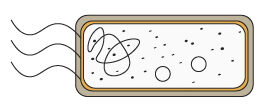 |
| Virus | Viruses live and reproduce rapidly inside cells. Virus will cause cell damage. |  |
| Fungi | Some fungi grow on or inside the body, damaging tissues. | 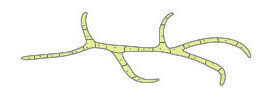 |
| Protist | Protists make us ill by acting as parasites they live inside our body, feeding on our cells | 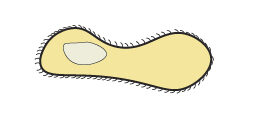 |
Transmission of disease
Communicable diseases can be spread by:
| Transmission method | How the pathogen is transmitted | Examples of diseases that are transmitted this way |
|---|---|---|
| By air (droplet infection) | An infected individual such as a human will cough or sneeze to expel droplets that contain the pathogen. An uninfected individual will breathe in these droplets and become infected. Many plant pathogens such as bacteria, viruses and fungal spores are transferred from one plant to another by air. | Humans: Influenza Covid Plants: Rose black spot |
| Direct contact | An uninfected organism makes physical contact with either infected organism, or a surface that is contaminated with pathogens. In animals many sexually transmitted infections are transmitted this way by direct contact of skin or mucus membranes. Plant pathogens can be transmitted by diseased plant material making contact with uninfected plant material. Animals can act as vectors by transferring pathogens from an infected individual to an uninfected individual. | Sexually transmitted infections such as syphilis or chlamydia Plant diseases such as tobacco mosaic virus The female Anopheles mosquito transfers the protist Plasmodium between an individual infected with malaria and an uninfected individual. So, the mosquito acts as a vector. |
| By water | Animals consuming either water contaminated with pathogens, or food which contains water that is contaminated with pathogens. Consumption of raw or undercooked food can also cause transmission of disease as the cooking process kills the pathogens Plants can be covered by water that is contaminated with fungal spores | In animals this can cause diarrhoea based diseases, cholera, typhoid or salmonella food poisoning. In rose plants it can cause rose black spot |
Reducing or Preventing the Spread of Disease.
There are several ways that communicable disease can be reduced, or prevented.
For Animals:
| Means of transmission control | Method to control transmission | Why it works |
|---|---|---|
| Hygiene | Wash hands Using disinfectants on surfaces Cooking food properly Cleaning surfaces | Kills or removes pathogens |
| Isolation or quarantine | Keeps infected people away from unifected individuals | Stops direct contact and transmission by air. |
| Vaccination | Gives a weakened or dead form of the pathogen | White blood cells, which form part of the bodies immune system will produce antibodies against the pathogen, so if infection occurs at a later point, the person will be immune. |
| Destroying vectors | Killing mosquitoes or preventing breeding of mosquitoes | Stops the organism that transfers the pathogen from passing on the pathogens |
| Safe sexual health practices (STIs) | Use condoms and regular testing of STIs. | Reduces the transfer of pathogens through bodily fluids. |
For Plants:
| Means of transmission control | Method to control transmission | Why it works |
|---|---|---|
| Destroying infected plants | Removing and burning diseased plants Removing infected leaves or branches | Removes the source of the pathogen so it cannot infect neighbouring plants |
| Crop rotation | Avoid planting the same crop in the same soil each year | Many pathogens stay in the soil; rotating crops breaks their life cycle and stops them spreading into the next year’s crop. |
| Using disease-resistant varieties | Planting crops bred to resist certain fungi, bacteria or viruses. | Fewer plants become infected, so the disease has limited opportunity to spread. |
| Good hygiene in fields | Cleaning tools before moving to another field or plant bed. Washing machinery and boots to remove soil and spores. | Stops pathogens being carried by people, tools, or vehicles. |
| Controlling vectors | Common plant disease vectors include aphids, whitefliies | Killing or reducing the number of pests will prevent them from transferring pathogens from plant to plant |
| Healthy planting practices | Leaving space between plants Avoiding overcrowding | This reduces contact between plants, so less direct contact of pathogens |
| Using chemical controls | Using fungicides, bactericides or insecticides | Reduces the number of pathogens or their carriers |
Practice Questions
1.State the definition of a pathogen
2. Explain how bacteria make us ill
3. State 3 ways that pathogens are transmitted
Factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis
Measuring & calculating rates of photosynthesis
Inverse square law and photosynthesis
Economics of enhancing the conditions in greenhouses
Investigating the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis