AQA GCSE Inverse square law and photosynthesis (Biology)
Inverse square law and photosynthesis
Light intensity is the amount of light energy hitting a surface per unit area per second.
Light intensity will have units of lux or W/m²
Light intensity decreases as distance from the source increases.

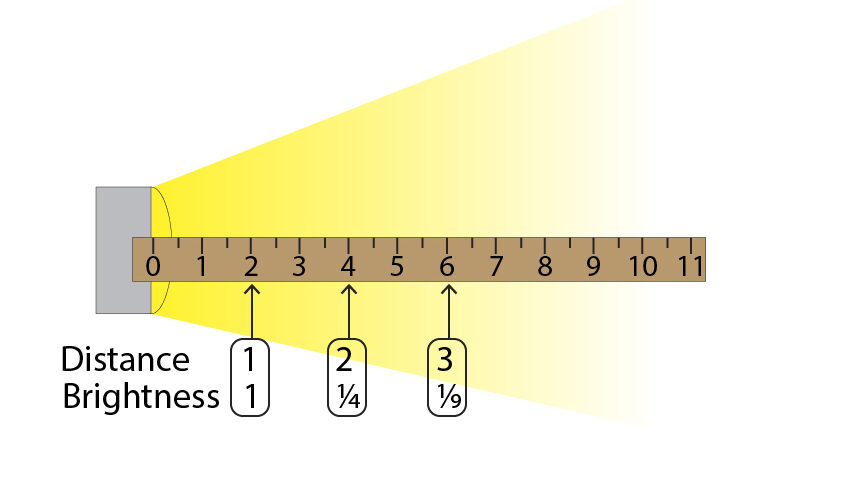
The diagram below shows the inverse square law. The distance in the boxes below the ruler is the RELATIVE Distance.
The actual distance is marked on the ruler.
In this case, we set an actual distance of 2cm to be a relative distance of 1.
This means that if the actual distance is doubled to 4cm, the relative distance is twice as far away, so it has a value of 2. The light intensity is then 1/22 = 1/4 of the original value where the relative distance was 1.
The table below the diagram will summarise the light intensity at different distances!
| Actual distance (cm) | Relative distance | Light intensity |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 2 | 1/22 = 1/4 |
| 6 | 3 | 1/32 = 1/9 |
| 8 | 4 | 1/42 = 1/16 |
Light intensity and Photosynthesis experiments
In photosynthesis experiments, as you move a light source further from a plant, the light intensity drops sharply.
If the pond weed is further from the lamp, the light intensity it receives will decrease, so fewer bubbles of oxygen gas will be produced per minute.
Looking at the data in the table, the inverse square law can be seen clearly. If the distance is doubled, the light intensity decreases by a factor of 4, or becomes 1/4 of its value, so the rate of photosynthesis does the same.

| Distance of pondweed from light source (cm) | Number of bubbles in 1 minute | Light intensity (relative units) |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 40 | 100 |
| 20 | 10 | 25 |
| 30 | 4 | 11 |
| 40 | 2 | 6 |
| 50 | 1 | 4 |
Practice Questions
1. State the formula for the inverse square law.
2. Fill in the table below to predict how changing distance will affect the amount of light intensity
| Effect on distance | Light intensity |
|---|---|
| Doubles | 1/4 of value |
| Triples | |
| Quadruples |
Factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis
Measuring & calculating rates of photosynthesis
Inverse square law and photosynthesis
Economics of enhancing the conditions in greenhouses
Investigating the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis