AQA GCSE Investigating the effect of pH on the rate of starch digestion by amylase (Biology)
Investigating the effect of pH on the rate of starch digestion by amylase.
We will investigate how changing the pH will affect the rate of starch digestion by amylase.
To carry out this practical a continuous sampling technique is used. This is where a sample is withdrawn from the reaction mixture at regular intervals e.g. 30 seconds and tested for starch.
Action of Amylase.
Amylase is an enzyme which speeds up the breakdown of starch into sugars.

Iodine solution is used to test for the presence of starch. When starch is present, iodine solution turns blue black. If starch is not present, then it will stay red-brown.

As the reaction progresses samples will be withdrawn at 30 second intervals and tested for starch.
The first samples will test positive for starch. However, later samples will test negative for starch as its been completely broken down. At this point we know the reaction is complete.
Method
1.A single drop of iodine solution is added to each of the wells in a spotting tile.
2. A measuring cylinder is used to transfer 2cm3 of amylase solution into a test tube.
3.Another measuring cylinder is used to transfer 1cm3 of pH 7 buffer solution to the same test tube. A buffer is a solution that helps to maintain a constant pH.
4. Another measuring cylinder is used to transfer 2cm3 of starch solution into a different test tube.
5. Both test tubes are placed into a water bath at 35oC. The solutions are allowed 5 minutes to reach the temperature of 35oC.
6. Once all the temperatures have equilibriated, the starch solution is poured into the mixture of amylase/pH buffer. A stopwatch is started.
7. Every 30 seconds, starting at 0 seconds a sample is removed from the reaction mixture and a drop is placed into one of the wells which contains iodine solution. Noting any colour change.
8. Initially the iodine solution will turn black, to indicate starch is present. Once the iodine solution stays brown and does not turn black any more stop the experiment and do not withraw anymore samples.
9. Repeat the experiment, but use different pH buffer solutions such as pH 5, and 9.
Results are recorded below the diagram.
The stage numbers in the diagram below refer to the number steps in the method above.

| Colour of iodine solution | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Time (seconds) | pH5 | pH7 | pH9 |
| 0 | Black | Black | Black |
| 30 | Black | Black | Black |
| 60 | Black | Black | Black |
| 90 | Black | Brown | Black |
| 120 | Black | Black | |
| 150 | Black | Black | |
| 180 | Brown | Brown | |
Calculating the rate of starch digestion
This type of reaction, is known as a clock reaction. This is where after a certain time period a change occurs. In this case the change is black to brown.
We use the following formula to calculate the rate.

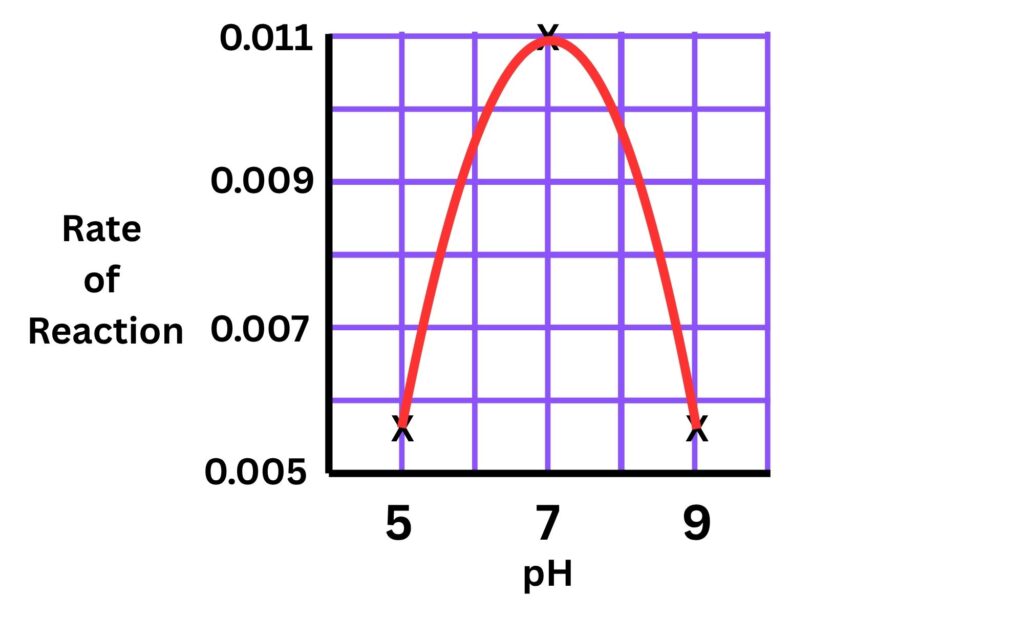
| pH | Time taken in seconds for the iodine solution to stay brown (seconds) | Rate of reaction (1/time) |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 180 | 0.0056 |
| 7 | 90 | 0.0111 |
| 9 | 180 | 0.0056 |
pH 7 has the highest rate of reaction.
Practice Questions
1.State the independent variable in experiment above
2. Give an example of a variable that has been controlled in the experiment above.
3. Suggest how the experiment could be made more accurate.
Factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis
Measuring & calculating rates of photosynthesis
Inverse square law and photosynthesis
Economics of enhancing the conditions in greenhouses
Investigating the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis